Correlation of multiple lipid and lipoprotein ratios with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic mellitus: A retrospective study
- PMID: 36875464
- PMCID: PMC9982122
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1127134
Correlation of multiple lipid and lipoprotein ratios with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic mellitus: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background and objective: The diagnostic value of lipid and lipoprotein ratios for NAFLD in newly diagnosed T2DM remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the relationships between lipid and lipoprotein ratios and the risk of NAFLD in subjects with newly diagnosed T2DM.
Methods: A total of 371 newly diagnosed T2DM patients with NAFLD and 360 newly diagnosed T2DM without NAFLD were enrolled in the study. Demographics variables, clinical history and serum biochemical indicators of the subjects were collected. Six lipid and lipoprotein ratios, including triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, cholesterol to HDL-C (TC/HDL-C) ratio, free fatty acid to HDL-C (FFA/HDL-C) ratio, uric acid to HDL-C (UA/HDL-C) ratio, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol to HDL-C (LDL-C/HDL-C) ratio, apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1 (APOB/A1) ratio, were calculated. We compared the differences in lipid and lipoprotein ratios between NAFLD group and non-NAFLD group, and further analyzed the correlation and diagnostic value of these ratios with the risk of NAFLD in the newly diagnosed T2DM patients.
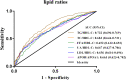
Results: The proportion of NAFLD in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM increased progressively over the range Q1 to Q4 of six lipid ratios, including the TG/HDL-C ratio, TC/HDL-C ratio, FFA/HDL-C ratio, UA/HDL-C ratio, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, and APOB/A1 ratio. After adjusting for multiple confounders, TG/HDL-C, TC/HDL-C, UA/HDL-C, LDL-C/HDL-C and APOB/A1 were all strongly correlated with the risk of NAFLD in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM. In patients with newly-onset T2DM, the TG/HDL-C ratio was the most powerful indicator for the diagnosis of NAFLD among all six indicators, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.732 (95% CI 0.696-0.769). In addition, TG/HDL-C ratio>1.405, with a sensitivity of 73.8% and specificity of 60.1%, had a good diagnostic ability for NAFLD in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.
Conclusions: The TG/HDL-C ratio may be an effective marker to help identify the risk of NAFLD in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.
Keywords: NAFLD; TG/HDL-C ratio; lipid ratios; lipoprotein ratios; newly diagnosed T2DM.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Kong, Ye, Zong, Hu, Xu, Fang, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a significant predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver: Jinchang cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Feb 11;18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0984-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30744645 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of traditional and non-traditional lipid indicators in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Japanese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Oct 7;21(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01712-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36207744 Free PMC article.
-
Higher serum uric acid to HDL-cholesterol ratio is associated with onset of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 21;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02263-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35448944 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Relationship Between Lipid Ratios and the Risk of Carotid Plaque.Angiology. 2025 Feb 14:33197251316624. doi: 10.1177/00033197251316624. Online ahead of print. Angiology. 2025. PMID: 39949279 Review.
-
Association between triglyceride to HDL cholesterol ratio and a risk of diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lab Med. 2025 Jan 6;56(1):1-6. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmae052. Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39066659
Cited by
-
Associations of nontraditional lipoprotein ratios with future cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jun 15;16(6):104120. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.104120. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40548282 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfosuccinimidyl oleate ameliorates the high-fat diet-induced obesity syndrome by reducing intestinal and hepatic absorption.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 26;14:1193006. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1193006. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37305546 Free PMC article.
-
Triglycerides to apolipoprotein A1 ratio: an effective insulin resistance-associated index in identifying metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 23;15:1384059. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1384059. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39764250 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota and protein-to-protein ratios in NAFLD: insights from Mendelian randomization and murine studies.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 18;12:1597390. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1597390. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40756562 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the incidence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 1;24(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03471-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39487389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Targher G, Bertolini L, Rodella S, Zoppini G, Lippi G, Day C, et al. . Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and proliferative/laser-treated retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. (2008) 51:444–50. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0897-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

