Perspective: The viscoelastic properties of biofilm infections and mechanical interactions with phagocytic immune cells
- PMID: 36875516
- PMCID: PMC9978752
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1102199
Perspective: The viscoelastic properties of biofilm infections and mechanical interactions with phagocytic immune cells
Abstract
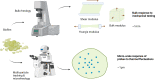
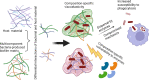
Biofilms are viscoelastic materials that are a prominent public health problem and a cause of most chronic bacterial infections, in large part due to their resistance to clearance by the immune system. Viscoelastic materials combine both solid-like and fluid-like mechanics, and the viscoelastic properties of biofilms are an emergent property of the intercellular cohesion characterizing the biofilm state (planktonic bacteria do not have an equivalent property). However, how the mechanical properties of biofilms are related to the recalcitrant disease that they cause, specifically to their resistance to phagocytic clearance by the immune system, remains almost entirely unstudied. We believe this is an important gap that is ripe for a large range of investigations. Here we present an overview of what is known about biofilm infections and their interactions with the immune system, biofilm mechanics and their potential relationship with phagocytosis, and we give an illustrative example of one important biofilm-pathogen (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) which is the most-studied in this context. We hope to inspire investment and growth in this relatively-untapped field of research, which has the potential to reveal mechanical properties of biofilms as targets for therapeutics meant to enhance the efficacy of the immune system.
Keywords: biofilm; immune system; neutrophil; phagocytosis; rheology; viscoelasticity.
Copyright © 2023 Wells, Schneider, Bhattarai, Currie, Chavez, Christopher, Rumbaugh and Gordon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baniasadi M., Xu Z., Gandee L., Du Y., Lu H., Zimmern P., Minary-Jolandan M., et al. . (2014). Nanoindentation of pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial biofilm using atomic force microscopy. Materials Res. Express 1 (4), 045411. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/1/4/045411 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

