MICAL-mediated oxidation of actin and its effects on cytoskeletal and cellular dynamics
- PMID: 36875759
- PMCID: PMC9982024
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1124202
MICAL-mediated oxidation of actin and its effects on cytoskeletal and cellular dynamics
Abstract
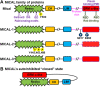
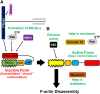
Actin and its dynamic structural remodelings are involved in multiple cellular functions, including maintaining cell shape and integrity, cytokinesis, motility, navigation, and muscle contraction. Many actin-binding proteins regulate the cytoskeleton to facilitate these functions. Recently, actin's post-translational modifications (PTMs) and their importance to actin functions have gained increasing recognition. The MICAL family of proteins has emerged as important actin regulatory oxidation-reduction (Redox) enzymes, influencing actin's properties both in vitro and in vivo. MICALs specifically bind to actin filaments and selectively oxidize actin's methionine residues 44 and 47, which perturbs filaments' structure and leads to their disassembly. This review provides an overview of the MICALs and the impact of MICAL-mediated oxidation on actin's properties, including its assembly and disassembly, effects on other actin-binding proteins, and on cells and tissue systems.
Keywords: MICAL1; MICAL2; MICAL3; MsrB; SelR; plexin; rab; semaphorin.
Copyright © 2023 Rajan, Terman and Reisler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The MICALs are a Family of F-actin Dismantling Oxidoreductases Conserved from Drosophila to Humans.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17943-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343822 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Production of the Mical Redox Domain for Enzymology and F-actin Disassembly Assays.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 17;22(4):1991. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041991. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671465 Free PMC article.
-
Catastrophic disassembly of actin filaments via Mical-mediated oxidation.Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 19;8(1):2183. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02357-8. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29259197 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of protein function by reversible methionine oxidation and the role of selenoprotein MsrB1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Oct 1;23(10):814-22. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6385. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 26181576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of MICAL family proteins - from actin oxidation to membrane trafficking during cytokinesis.J Cell Sci. 2017 May 1;130(9):1509-1517. doi: 10.1242/jcs.202028. Epub 2017 Apr 3. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28373242 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 budding requires cortical actin disassembly by the oxidoreductase MICAL1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 26;121(48):e2407835121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407835121. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39556735 Free PMC article.
-
F-actin disassembly by the oxidoreductase MICAL1 promotes mechano-dependent VWF-GPIbα interaction in platelets.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 10;16(1):7375. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62487-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40783397 Free PMC article.
-
Mical1 deletion in tyrosinase expressing cells affects mouse running gaits.Genes Brain Behav. 2024 Oct;23(5):e70004. doi: 10.1111/gbb.70004. Genes Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39344934 Free PMC article.
-
Disassembly of bundled F-actin and cellular remodeling via an interplay of Mical, cofilin, and F-actin crosslinkers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 26;120(39):e2309955120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309955120. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37725655 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of MICAL autoinhibition.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 12;15(1):9810. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54131-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39532862 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

