A review on the role of long non-coding RNA prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 (PART1) in the etiology of different disorders
- PMID: 36875771
- PMCID: PMC9974648
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1124615
A review on the role of long non-coding RNA prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 (PART1) in the etiology of different disorders
Abstract
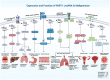
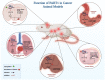
LncRNA prostate androgen-regulated transcript 1 (PART1) is an important lncRNA in the carcinogenesis whose role has been firstly unraveled in prostate cancer. Expression of this lncRNA is activated by androgen in prostate cancer cells. In addition, this lncRNA has a role in the pathogenesis intervertebral disc degeneration, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and Parkinson's disease. Diagnostic role of PART1 has been assessed in some types of cancers. Moreover, dysregulation of PART1 expression is regarded as a prognostic factor in a variety of cancers. The current review provides a concise but comprehensive summary of the role of PART1 in different cancers and non-malignant disorders.
Keywords: PART1; biomarker; cancer; diagnsotic marker; lncRNA.
Copyright © 2023 Ghafouri-Fard, Harsij, Hussen, Abdullah, Baniahmad, Taheri and Sharifi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of lncRNA PART1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and associated underlying mechanism.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Feb;21(2):131. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9563. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33376513 Free PMC article.
-
Long non‑coding RNA PART1: dual role in cancer.Hum Cell. 2022 Sep;35(5):1364-1374. doi: 10.1007/s13577-022-00752-y. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Hum Cell. 2022. PMID: 35864416 Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA PART1 Exerts Tumor Suppressive Functions in Glioma via Sponging miR-190a-3p and Inactivation of PTEN/AKT Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Feb 4;13:1073-1086. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S232848. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32099409 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA PART1 modulates toll-like receptor pathways to influence cell proliferation and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells.Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 28;399(4):387-395. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2017-0255. Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29261512
-
A review on the role of PCA3 lncRNA in carcinogenesis with an especial focus on prostate cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Mar;231:153800. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153800. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35180654 Review.
Cited by
-
lncRNA PART1 improves sevoflurane-induced impairments in learning and cognitive function by regulating miR-16-5p expression and reducing neuroinflammation.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jan 26;14(1):tfaf009. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf009. eCollection 2025 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39872305
-
Identification and validation of expression and functions of ferroptosis-related gene HILPDA in early-onset preeclampsia placentas.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 11;16:1627057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1627057. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40861438 Free PMC article.
-
Single cell-transcriptomic analysis informs the lncRNA landscape in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer.NPJ Genom Med. 2024 Feb 23;9(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s41525-024-00401-3. NPJ Genom Med. 2024. PMID: 38396008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cruickshank B. M., Wasson M. D., Brown J. M., Fernando W., Venkatesh J., Walker O. L., et al. (2021). LncRNA PART1 promotes proliferation and migration, is associated with cancer stem cells, and alters the miRNA landscape in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13 (11), 2644. PubMed PMID: 34072264. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC8198907. Epub 2021/06/03. eng. 10.3390/cancers13112644 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

