The complete chloroplast genome of Elsholtzia fruticosa (D. Don) Rehd. (Labiatae), an ornamental plant with high medicinal value
- PMID: 36876144
- PMCID: PMC9980026
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2023.2183069
The complete chloroplast genome of Elsholtzia fruticosa (D. Don) Rehd. (Labiatae), an ornamental plant with high medicinal value
Abstract
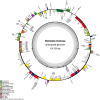
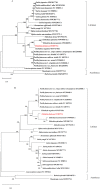
Elsholtzia fruticosa is an ornamental plant with high medicinal value. In this study, we sequenced and analyzed the complete chloroplast (cp) genome of the species. The complete cp sequence is 151,550 bp, including the large single-copy (LSC) region of 82,778 bp, the small single-copy (SSC) region of 17,492 bp, and a pair of invert repeats (IRs) regions of 25,640 bp. It encodes 132 unique genes in total, including 87 protein-coding genes, 37 transfer RNA genes (tRNAs), and eight ribosomal RNA genes (rRNAs). The comparative analysis of complete cp genomes showed that the genomic structure and gene order of E. fruticosa cps were conserved. The sequences of rps15, rps19, ycf1, ycf3, ycf15, psbL, psaI, trnG-UCC, trnS-GCU, trnR-UCU, trnL-UAG, trnP-UG, and trnL-UAA serve as hotspots for developing the DNA barcoding of Elsholtzia species. There are 49 SSR loci in the cp genome of E. fruticosa, among which the repeat numbers of mononucleotide, dinucleotide, trinucleotide, tetranucleotide, and pentanucleotides SSR are 37, 9, 3, 0, and 0, respectively. A total of 50 repeats were detected, including 15 forward repeats, seven reverse repeats, 26 palindromic repeats, and two complementary repeats. Phylogenetic analysis based on the complete cp genome and protein-coding DNA sequences of 26 plants indicates that E. fruticosa has a dose relationship with E. splendens and E. byeonsanensis.
Keywords: Elsholtzia fruticosa; chloroplast genome; phylogenetic analysis.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative genome analysis revealed gene inversions, boundary expansions and contractions, and gene loss in the Stemona sessilifolia (Miq.) Miq. chloroplast genome.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 18;16(6):e0247736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247736. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34143785 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and comparative analysis of Mesona chinensis Benth chloroplast genome reveals DNA barcode regions for species identification.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Aug;22(4):467-479. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00846-8. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35318559
-
Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major economic species, Ziziphus jujuba (Rhamnaceae).Curr Genet. 2017 Feb;63(1):117-129. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0612-4. Epub 2016 May 20. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27206980
-
Complete chloroplast genome of Stephania tetrandra (Menispermaceae) from Zhejiang Province: insights into molecular structures, comparative genome analysis, mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationships.BMC Genomics. 2021 Dec 6;22(1):880. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08193-x. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34872502 Free PMC article.
-
Amorpha fruticosa - A Noxious Invasive Alien Plant in Europe or a Medicinal Plant against Metabolic Disease?Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 8;8:333. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00333. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28642702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methanol extract of Elsholtzia fruticosa promotes 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation.J Anim Sci Technol. 2024 Jan;66(1):204-218. doi: 10.5187/jast.2024.e6. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38618027 Free PMC article.
-
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of an invasive plant, Tragopogon dubius Scopoli (asteraceae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024 Mar 13;9(3):352-356. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2024.2329668. eCollection 2024. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024. PMID: 38487811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiryousefi A, Hyvönen J, Poczai P.. 2018. IRscope: an online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics. 34(17):3030–3031. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Chen J, Xu Y, Wang X, Li J.. 2022. Elsholtzia: a genus with antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory advantages. J Ethnopharmacol. 297:115549. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
