Has the therapeutical ceiling been reached in Crohn's disease randomized controlled trials? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36876515
- PMCID: PMC10039796
- DOI: 10.1002/ueg2.12366
Has the therapeutical ceiling been reached in Crohn's disease randomized controlled trials? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: The availability of biological agents for inflammatory bowel disease has increased over the past years. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to explore time trends in clinical response and clinical remission rates in Crohn's disease (CD) patients treated with biologics while discussing the need for new strategies.
Methods: MEDLINE, Cochrane, and ISI Web of Science databases were searched for randomized placebo-controlled trials with biological agents in moderate-to-severe CD patients. Sub-group and meta-regression analyses compared treatment and placebo by calculating the pooled odds ratios of clinical remission and clinical response, across time categories and publication year. We also estimated the proportion of patients achieving clinical remission and clinical response by comparing both groups according to the publication year.
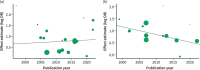
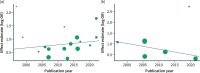
Results: Twenty-five trials were included in the systematic review, which enrolled 8879 patients between 1997 and 2022. The clinical remission and clinical response odds, in induction and maintenance, have been constant over time, as no statistically significant differences were found between time categories (interaction p-values: clinical remission [induction, p = 0.19; maintenance, p = 0.24]; clinical response [induction, p = 0.43; maintenance, p = 0.59]). In meta-regression analyses, publication year did not influence these outcomes (clinical remission [induction, OR 1.01{95% CI 0.97-1.05}, p = 0.72; clinical response [induction, OR 1.01{95% CI 0.97-1.04]; p = 0.63; maintenance, OR 1.03{95% CI 0.98-1.07}; p = 0.21]), with the exception of clinical remission in maintenance studies, which presented a decreased effect (odds ratio 0.97{95% CI 0.94-1.00}, p = 0.03]).
Conclusions: Our review highlights that the odds of clinical outcomes in CD patients receiving biological treatment relative to placebo have been stable in the last decades.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; RCT; biologics; clinical remission; clinical response; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trial; systematic review; therapeutical ceiling; therapy.
© 2023 The Authors. United European Gastroenterology Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of United European Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Fernando Magro served as a speaker and received honoraria from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Abbvie, Vifor, Falk, Laboratórios Vitória, Ferring, Hospira, and Biogen; Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet reports personal fees from Merck, Abbvie, Janssen, Genentech, Mitsubishi, Ferring, Norgine, Tillots, Vifor, Hospira/Pfizer, Celltrion, Takeda, Biogaran, Boerhinger‐Ingelheim, Lilly, HAC‐Pharma, Index Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Sandoz, For‐ward Pharma GmbH, Celgene, Biogen, Lycera, and Samsung Biosepsis; Silvio Danese served as a speaker, consultant and advisory board member for Schering‐Plough, Abbott (AbbVie) Laboratories, Merck, UCB Pharma, Ferring, Cellerix, Millenium Takeda, Nycomed, Pharmacosmos, Actelion, Alfa Wasserman, Genentech, Grunenthal, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Cosmo Pharmaceuticals, Vifor and Johnson and Johnson; Vipul Jairath has received consulting/advisory board fees from AbbVie, Alimentiv Inc (formerly Robarts Clinical Trials), Arena pharmaceuticals, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Asieris, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Ferring, Flagship Pioneering, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Mylan, Pandion, Pendopharm, Pfzer, Protagonist, Reistone Biopharma, Roche, Sandoz, Second Genome, Takeda, Teva, Topivert, and Vividion; speaker's fees from, Abbvie, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen Pfzer Shire, Takeda, and Fresenius Kabi; Axel Dignass has received has received research support or acted as a principal investigator for Abbvie, Celgene/BMS, Dr Falk Pharma, Gilead/Galapagos, Janssen, Pfizer and Takeda; has acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene/BMS, Celltrion, Dr Falk Pharma, Ferring, Fresenius Kabi, Janssen, MSD, Pharmacosmos, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, Tillotts, and Vifor; and has participated in speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Falk Foundation, Ferring, Janssen, MSD, Pharmacosmos, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, Tillotts, and Vifor; the other authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

