Non-target estrogenic screening of 60 pesticides, six plant protection products, and tomato, grape, and wine samples by planar chromatography combined with the planar yeast estrogen screen bioassay
- PMID: 36877263
- PMCID: PMC10766744
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-023-04605-x
Non-target estrogenic screening of 60 pesticides, six plant protection products, and tomato, grape, and wine samples by planar chromatography combined with the planar yeast estrogen screen bioassay
Abstract
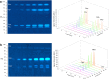
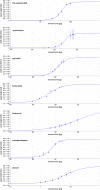
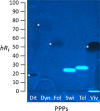
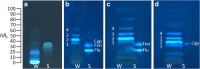
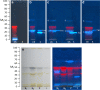
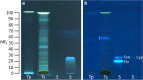
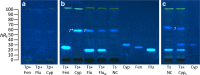
For non-target residue analysis of xenoestrogens in food, sophisticated chromatographic-mass spectrometric techniques lack in biological effect detection. Various in vitro assays providing sum values encounter problems when opposing signals are present in a complex sample. Due to physicochemical signal reduction, cytotoxic or antagonistic effect responses, the resulting sum value is falsified. Instead, the demonstrated non-target estrogenic screening with an integrated planar chromatographic separation differentiated opposing signals, detected and prioritized important estrogenic compounds, and directly assigned tentatively the responsible compounds. Sixty pesticides were investigated, ten of which showed estrogenic effects. Exemplarily, half-maximal effective concentrations and 17β-estradiol equivalents were determined. Estrogenic pesticide responses were confirmed in six tested plant protection products. In food, such as tomato, grape, and wine, several compounds with an estrogenic effect were detected. It showed that rinsing with water was not sufficient to remove selected residues and illustrated that, though not usually performed for tomatoes, peeling would be more appropriate. Though not in the focus, reaction or breakdown products that are estrogenic were detected, underlining the great potential of non-target planar chromatographic bioassay screening for food safety and food control.
Keywords: Bioautography; Endocrine-disrupting compounds; Food safety; Planar yeast estrogen screen; Residue analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market and repealing Council Directives 79/117/EEC and 91/414/EEC; 2009.
-
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 February 2005 on maximum residue levels of pesticides in or on food and feed of plant and animal origin and amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC; 2005.
-
- EU pesticides database. https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database_en. Accessed 22 Sep 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

