Identification and functional analysis of protein secreted by Alternaria solani
- PMID: 36877688
- PMCID: PMC9987770
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281530
Identification and functional analysis of protein secreted by Alternaria solani
Abstract
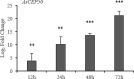
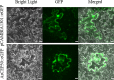
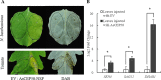
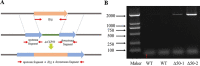
Early blight, caused by the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria solani, is an important foliar disease that causes major yield losses of potato. Effector proteins secreted by pathogens to host cells can inhibit host immune response to pathogens. Currently, the function of effector proteins secreted by A. solani during infection is poorly understood. In this study, we identified and characterized a novel candidate effector protein, AsCEP50. AsCEP50 is a secreted protein that is highly expressed throughout the infection stages of A. solani. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana and tomato demonstrated that AsCEP50 is located on the plasma membrane of N. benthamiana and regulates senescence-related genes, resulting in the chlorosis of N. benthamiana and tomato leaves. Δ50 mutants were unaffected in vegetative growth, spore formation and mycelium morphology. However, the deletion of AsCEP50 significantly reduced virulence, melanin production and penetration of A. solani. These results strongly supported that AsCEP50 is an important pathogenic factor at the infection stage and contributes to the virulence of Alternaria solani.
Copyright: © 2023 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alternaria solani Effector AsCEP20, Essential for Virulence, Targets Potato StFtsH4 Protein to Suppress Plant Disease Resistance.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 Jun;26(6):e70109. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70109. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40518751 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of effector CEP112 that promotes the infection of necrotrophic Alternaria solani.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Sep 29;22(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03845-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36171557 Free PMC article.
-
Alternaria solani effectors AsCEP19 and AsCEP20 reveal novel functions in pathogenicity and conidiogenesis.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0421423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04214-23. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38912810 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence of the potato pathogenic fungus Alternaria solani HWC-168 reveals clues for its conidiation and virulence.BMC Microbiol. 2018 Nov 6;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1324-3. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30400851 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctionality of AsCFEM6 and AsCFEM12 effectors from the potato early blight pathogen Alternaria solani.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;257(Pt 1):128575. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128575. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38048930
Cited by
-
Alternaria diseases on potato and tomato.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Mar;25(3):e13435. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13435. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38476108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternaria solani Effector AsCEP20, Essential for Virulence, Targets Potato StFtsH4 Protein to Suppress Plant Disease Resistance.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 Jun;26(6):e70109. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70109. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40518751 Free PMC article.
-
A glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein from Alternaria alternata triggers cell death and negatively modulates immunity responses in chrysanthemum.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Nov 18;43(12):283. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03372-y. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39557715
-
Network analyses predict major regulators of resistance to early blight disease complex in tomato.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 6;24(1):641. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05366-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38971719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nehela Y, Taha NA, Elzaawely AA, Xuan TD, A Amin M, Ahmed ME, et al.. Benzoic acid and its hydroxylated derivatives suppress early blight of tomato (Alternaria solani) via the induction of salicylic acid biosynthesis and enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant defense machinery. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(8):663. doi: 10.3390/jof7080663 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beliaev DV, Yuorieva NO, Tereshonok DV, Tashlieva II, Derevyagina MK, Meleshin AA, et al.. High resistance of potato to early blight is achieved by expression of the Pro–SmAMP1 gene for hevein-like antimicrobial peptides from common chickweed (Stellaria media). Plants (Basel). 2021;10(7):1395. doi: 10.3390/plants10071395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dita MA, Brommonschenkel SH, Matsuoka K, Mizubuti ESG. Histopathological study of the Alternaria solani infection process in potato cultivars with different levels of early blight resistance. Journal of Phytopathology. 2007;155(7-8):462–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0434.2007.01258.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

