Effect of B12 and folate deficiency in hypomethylation of Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 gene and severity of disease among the acute respiratory distress syndrome patients
- PMID: 36877757
- PMCID: PMC10098068
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24846
Effect of B12 and folate deficiency in hypomethylation of Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 gene and severity of disease among the acute respiratory distress syndrome patients
Abstract
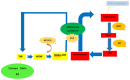
Background: Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) is the most important receptor and has important role in the entry of corona virus to the host cells. The present study aimed to investigate the different mechanisms involved in the expression regulation of this gene among the COVID-19 patients.
Methods: A total of 140 patients with COVID-19 (n = 70 mild COVID-19, n = 70 ARDS) and 120 controls were recruited. The expression of ACE-2 and miRNAs was evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR), and methylation of CpG dinucleotides in the ACE2 promoter was quantified using bisulfite pyro-sequencing. Finally, different polymorphisms of the ACE-2 gene were studied by Sanger sequencing.
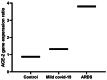
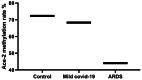
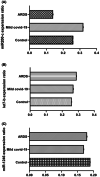
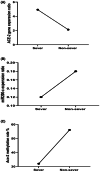
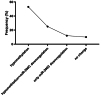
Results: Our results showed a significant high expression of the ACE-2 gene in the blood samples of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients (3.8 ± 0.77) in comparison with controls (0.88 ± 0.12; p < 0.03). The methylation rate of the ACE-2 gene in ARDS patients was 14.07 ± 6.1 compared with controls (72.3 ± 5.1; p < 0.0001). Among the four studied miRNAs, only miR200c-3p showed significant downregulation in ARDS patients (0.14 ± 0.1) in comparison with controls (0.32 ± 0.17; p < 0.001). We did not see a substantial difference in the frequency of rs182366225 C>T and rs2097723 T>C polymorphisms between patients and controls (p > 0.05). There was a significant correlation between B12 (R = 0.32, p < 0.001), folate (R = 0.37, p < 0.001) deficiency, and hypo-methylation of the ACE-2 gene.
Conclusion: These results for the first time indicated that among the different mechanisms of ACE-2 expression regulation, its promoter methylation is very crucial and can be affected by factors involved in one-carbon metabolisms such as B9 and B12 vitamins deficiency.
Keywords: ACE-2; B vitamins; COVID-19; expression regulation; hypomethylation.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation . Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected‐Interim guidance.
-
- Zhang YH, Gong LK, Ren J, et al. The role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in the pathologic pathway of SARS. Chin J Pharm Toxicol. 2007;21:72‐76.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

