ctDNA and residual cancer burden are prognostic in triple-negative breast cancer patients with residual disease
- PMID: 36878909
- PMCID: PMC9988835
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-023-00512-7
ctDNA and residual cancer burden are prognostic in triple-negative breast cancer patients with residual disease
Abstract
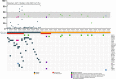
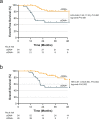
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients with residual disease (RD) after neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAST) are at high risk for recurrence. Biomarkers to risk-stratify patients with RD could help individualize adjuvant therapy and inform future adjuvant therapy trials. We aim to investigate the impact of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) status and residual cancer burden (RCB) class on outcomes in TNBC patients with RD. We analyze end-of-treatment ctDNA status in 80 TNBC patients with residual disease who are enrolled in a prospective multisite registry. Among 80 patients, 33% are ctDNA positive (ctDNA+) and RCB class distribution is RCB-I = 26%, RCB-II = 49%, RCB-III = 18% and 7% unknown. ctDNA status is associated with RCB status, with 14%, 31%, and 57% of patients within RCB-I, -II, and -III classes demonstrating ctDNA+ status (P = 0.028). ctDNA+ status is associated with inferior 3-year EFS (48% vs. 82%, P < 0.001) and OS (50% vs. 86%, P = 0.002). ctDNA+ status predicts inferior 3-year EFS among RCB-II patients (65% vs. 87%, P = 0.044) and shows a trend for inferior EFS among RCB-III patients (13% vs. 40%, P = 0.081). On multivariate analysis accounting for T stage and nodal status, RCB class and ctDNA status independently predict EFS (HR = 5.16, P = 0.016 for RCB class; HR = 3.71, P = 0.020 for ctDNA status). End-of-treatment ctDNA is detectable in one-third of TNBC patients with residual disease after NAST. ctDNA status and RCB are independently prognostic in this setting.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.P.O.: Consulting honoraria from Pfizer, Puma Biotechnology, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo, Astra Zeneca, and Seattle Genetics; A.K.G.: Co-founder of Sinochips Diagnostics, serves as a scientific advisory board member to Biovica, Clara Biotech, and Sinochips Diagnostics, and receives research funding from Predicine and VITRAC Therapeutics; P.S.: Research funding from Novartis, Merck, Gilead, and BMS; serves as a consultant/advisor to AstraZeneca, Novartis, Merck, GSK, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Genzyme; and receives royalties from UpToDate. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mayer IA, et al. Randomized phase III postoperative trial of platinum-based chemotherapy versus capecitabine in patients with residual triple-negative breast cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: ECOG-ACRIN EA1131. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39:2539–2551. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00976. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P20 GM130423/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2TR002367/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- P20GM130423/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- P30CA168524/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

