Falcaria vulgaris leaves extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid media
- PMID: 36879043
- PMCID: PMC9988855
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-30571-6
Falcaria vulgaris leaves extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid media
Abstract
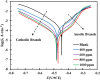
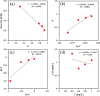
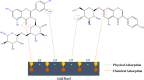
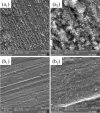
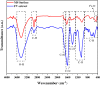
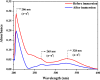
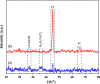
Undoubtedly, metal corrosion is one of the most challenging problems faced by industries. Introducing corrosion inhibitors is a reasonable approach to protecting the metal surface. Due to environmental concerns and the toxicity of industrial organic corrosion inhibitors, researchers are continually exploring acceptable replacements. The current study focused on the application of Falcaria Vulgaris (FV) leaves extract to mitigate mild steel (MS) corrosion in a 1 M HCl environment. The polarization findings demonstrated that the corrosion current density decreased from 264.0 µA/cm2 (for the sample submerged in the blank solution) to 20.4 µA/cm2 when the optimal concentration of 800 ppm of FV leaves extract was added to the acid solution. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis revealed an inhibition efficiency of 91.3% at this concentration after 6 h of immersion. It was determined by analyzing several adsorption isotherms that this corrosion inhibitor obeys the Frumkin isotherm. AFM, FE-SEM, and GIXRD surface analyses also supported the findings that adding FV leaves extract can reduce metal damage by adsorption on the metal surface.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
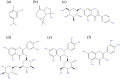
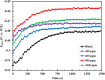
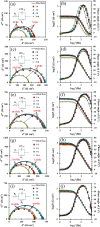
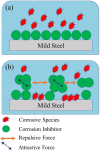

References
-
- Sun X, Qiang Y, Hou B, Zhu H, Tian H. Cabbage extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for X70 steel in hydrochloric acid medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2022;362:119733. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119733. - DOI
-
- Honarvar Nazari M, et al. Nanocomposite organic coatings for corrosion protection of metals: A review of recent advances. Prog. Org. Coatings. 2022;162:106573. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106573. - DOI
-
- Ouakki M, Galai M, Cherkaoui M. Imidazole derivatives as efficient and potential class of corrosion inhibitors for metals and alloys in aqueous electrolytes: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022;345:117815. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117815. - DOI
-
- Khadom AA, Abd AN, Ahmed NA. Xanthium strumarium leaves extracts as a friendly corrosion inhibitor of low carbon steel in hydrochloric acid: Kinetics and mathematical studies. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2018;25:13–21.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

