Higher plasma levels of thymosin-α1 are associated with a lower waning of humoral response after COVID-19 vaccination: an eight months follow-up study in a nursing home
- PMID: 36879319
- PMCID: PMC9986663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12979-023-00334-y
Higher plasma levels of thymosin-α1 are associated with a lower waning of humoral response after COVID-19 vaccination: an eight months follow-up study in a nursing home
Abstract
Background: Older people achieve lower levels of antibody titers than younger populations after Covid-19 vaccination and show a marked waning humoral immunity over time, likely due to the senescence of the immune system. Nevertheless, age-related predictive factors of the waning humoral immune response to the vaccine have been scarcely explored. In a cohort of residents and healthcare workers from a nursing home that had received two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine, we measured specific anti-S antibodies one (T1), four (T4), and eight (T8) months after receiving the second dose. Thymic-related functional markers, including thymic output, relative telomere length, and plasma thymosin-α1 levels, as well as immune cellular subsets, and biochemical and inflammatory biomarkers, were determined at T1, and tested for their associations with the magnitude of the vaccine response (T1) and the durability of such response both, at the short- (T1-T4) and the long-term (T1-T8). We aimed to identify age-related factors potentially associated with the magnitude and persistence of specific anti-S immunoglobulin G (IgG)-antibodies after COVID-19 vaccination in older people.
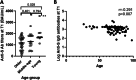
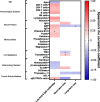
Results: Participants (100% men, n = 98), were subdivided into three groups: young (< 50 years-old), middle-age (50-65 years-old), and older (≥65 years-old). Older participants achieved lower antibody titers at T1 and experienced higher decreases in both the short- and long-term. In the entire cohort, while the magnitude of the initial response was mainly associated with the levels of homocysteine [β (95% CI); - 0.155 (- 0.241 to - 0.068); p = 0.001], the durability of such response at both, the short-term and the long-term were predicted by the levels of thymosin-α1 [- 0.168 (- 0.305 to - 0.031); p = 0.017, and - 0.123 (- 0.212 to - 0.034); p = 0.008, respectively].
Conclusions: Higher plasma levels of thymosin-α1 were associated with a lower waning of anti-S IgG antibodies along the time. Our results suggest that plasma levels of thymosin-α1 could be used as a biomarker for predicting the durability of the responses after COVID-19 vaccination, possibly allowing to personalize the administration of vaccine boosters.
Keywords: Antibody waning; BNT162b2 vaccine; Immunesenescence; Inflammaging; Magnitude and persistence of humoral response; Nursing home; RTL; Sj/β-TRECs ratio; Thymic-function; Thymosin-α1.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factors associated with the humoral response after three doses of COVID-19 vaccination in kidney transplant recipients.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1099079. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1099079. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875099 Free PMC article.
-
Durability of Immune Response After COVID-19 Booster Vaccination and Association With COVID-19 Omicron Infection.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Sep 1;5(9):e2231778. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31778. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36107426 Free PMC article.
-
BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine and correlates of humoral immune responses and dynamics: a prospective, single-centre, longitudinal cohort study in health-care workers.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Sep;9(9):999-1009. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00220-4. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34224675 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and Cellular Response after mRNA Vaccination in Nursing Homes: Influence of Age and of History of COVID-19.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;10(3):383. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10030383. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35335015 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world serological responses to extended-interval and heterologous COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in frail, older people (UNCoVER): an interim report from a prospective observational cohort study.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022 Mar;3(3):e166-e175. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00012-5. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022. PMID: 35224524 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Markers of T-cell dysfunction and not inflammaging predict the waning of humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA booster vaccination in people with HIV.AIDS. 2024 Nov 15;38(14):1987-1990. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000004010. Epub 2024 Oct 31. AIDS. 2024. PMID: 39474654 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of SARS COV-2 IgG Anti-N as an Independent Marker of Exposure to SARS COV-2 in an Unvaccinated West African Population.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023 Aug 14;109(4):890-894. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0179. Print 2023 Oct 4. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023. PMID: 37580023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: an observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet. 2021;397:1819–1829. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00947-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

