Practice of Kangaroo Mother Care Among Low-Birth-Weight Infants Discharged from Health Facilities and Its Outcome in Mekelle City, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia
- PMID: 36879617
- PMCID: PMC9985394
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S396471
Practice of Kangaroo Mother Care Among Low-Birth-Weight Infants Discharged from Health Facilities and Its Outcome in Mekelle City, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Kangaroo mother care is a proven intervention shown to be effective in reducing neonatal mortality among low-birth-weight infants. The paucity of evidence regarding the practice at home can be highlighted. This study aimed to assess the practice and outcome of kangaroo mother care at home among mothers having low-birth-weight infants discharged from two hospitals in Mekelle, Tigray, Ethiopia.
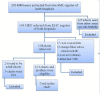
Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted among 101 paired mothers and low-birth-weight neonates discharged from Ayder and Mekelle Hospitals. Non-probability purposive sampling was used to select 101 infants. Data were collected from patient charts in both hospitals using interviewer-administered structured questionnaire, anthropometric measurements and were then analyzed using SPSS version 20. Characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Bivariate analysis was used, and variables with p-value <0.25 were exported to multivariable logistic regression and statistical significance was set at a p-value <0.05.
Results: Kangaroo mother care was continued at home in 99% of the infants. Three of the 101 infants died before the age of 4 months with a possible cause of death from respiratory failure. Exclusive breastfeeding was provided for 67% of the infants, and it was higher in infants who started kangaroo mother care within 24 hours of life (AOR 3.8, 95% CI 1.07-13.25). Malnutrition was higher in those with birth weight <1500 grams (AOR 7.3,95% CI 1.63-32.59); small for gestational age (AOR 4.8,95% CI 1.41-16.31) and those provided kangaroo mother care for <8 hours per day (AOR 4.5,95% CI 1.40-16.31).
Conclusion: Early initiation and prolonged duration of kangaroo mother care were associated with increased exclusive breastfeeding practice and decreased incidence of malnutrition. Kangaroo mother care should be promoted at the community level.
Keywords: exclusive breastfeeding; kangaroo mother care; low birth weight; malnutrition.
© 2023 Gidey et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHA Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Low Birth Weight Policy Brief. World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations on Interventions to Improve Preterm Birth Outcomes. World Health Organization; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Oxford University Press. Kangaroo Mother Care: Journal of Tropical Pediatrics. Vol. 45. Oxford University Press; 1999.
-
- Shanthi R, Sundari S. Effect of kangaroo mother care on the growth and morbidity pattern of low birth weight infants: a hospital based cross sectional study. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2020;7:728–732. doi: 10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20200583 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

