Piezo1-mediated M2 macrophage mechanotransduction enhances bone formation through secretion and activation of transforming growth factor-β1
- PMID: 36880296
- PMCID: PMC10472522
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13440
Piezo1-mediated M2 macrophage mechanotransduction enhances bone formation through secretion and activation of transforming growth factor-β1
Abstract
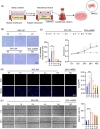
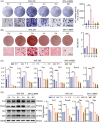
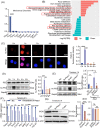
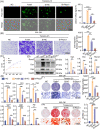
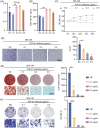
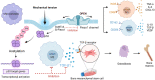
Macrophages are multifunctional immune system cells that are essential for the mechanical stimulation-induced control of metabolism. Piezo1 is a non-selective calcium channel expressed in multifarious tissues to convey mechanical signals. Here, a cellular model of tension was used to study the effect of mechanical stretch on the phenotypic transformation of macrophages and its mechanism. An indirect co-culture system was used to explore the effect of macrophage activation on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), and a treadmill running model was used to validate the mechanism in vivo for in vitro studies. p53 was acetylated and deacetylated by macrophages as a result of mechanical strain being detected by Piezo1. This process is able to polarize macrophages towards M2 and secretes transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1), which subsequently stimulates BMSCs migration, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. Knockdown of Piezo1 inhibits the conversion of macrophages to the reparative phenotype, thereby affecting bone remodelling. Blockade of TGF-β I, II receptors and Piezo1 significantly reduced exercise-increased bone mass in mice. In conclusion, we showed that mechanical tension causes calcium influx, p53 deacetylation, macrophage polarization towards M2 and TGF-β1 release through Piezo1. These events support BMSC osteogenesis.
© 2023 The Authors. Cell Proliferation published by Beijing Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Macrophages regulate angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling induced by mechanical loading through the Piezo1 pathway.J Bone Miner Res. 2025 Jun 3;40(6):725-737. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae198. J Bone Miner Res. 2025. PMID: 39657223
-
Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-β1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect.Cell Prolif. 2020 Oct;53(10):e12907. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12907. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32951298 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical force modulates macrophage proliferation via Piezo1-AKT-Cyclin D1 axis.FASEB J. 2022 Aug;36(8):e22423. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200314R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35775626 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 stretch-activated channel activity differs between murine bone marrow-derived and cardiac tissue-resident macrophages.J Physiol. 2024 Sep;602(18):4437-4456. doi: 10.1113/JP284805. Epub 2024 Apr 20. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38642051
-
Mechanosensitive Piezo1 protein as a novel regulator in macrophages and macrophage-mediated inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1149336. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1149336. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37334369 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Piezo1 in chronic inflammatory diseases and prospects for drug treatment (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):200. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13565. Epub 2025 May 16. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40376999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly-D,L-Lactic Acid Fillers Increase Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Volume by Promoting Adipogenesis in Aged Animal Skin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12739. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312739. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684448 Free PMC article.
-
SEC24D depletion induces osteogenic differentiation deficiency by inactivating the ATF6/TGF-β/Runx2 regulatory loop.Commun Biol. 2025 May 15;8(1):758. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08175-9. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40374976 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 Activation Drives Enhanced Collagen Synthesis in Aged Animal Skin Induced by Poly L-Lactic Acid Fillers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 30;25(13):7232. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137232. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000341 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte Platelet-Rich Plasma-Derived Exosomes Restrained Macrophages Viability and Induced Apoptosis, NO Generation, and M1 Polarization.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Nov;12(11):e70064. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70064. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39545659 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81670965/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970961/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82271002/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20191346/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- YJXYYJSDW4/JiangSu Province Capability Improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education-Jiangsu Provincial Research Hospital Cultivation Unit
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

