Robotics planning in minimally invasive surgery for adult degenerative scoliosis: illustrative case
- PMID: 36880510
- PMCID: PMC10550660
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE22520
Robotics planning in minimally invasive surgery for adult degenerative scoliosis: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Minimally invasive surgical techniques are changing the landscape in adult spinal deformity (ASD) surgery, enabling surgical correction to be achievable in increasingly medically complex patients. Spinal robotics are one technology that have helped facilitate this. Here the authors present an illustrative case of the utility of robotics planning workflow for minimally invasive correction of ASD.
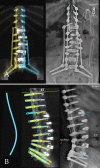
Observations: A 60-year-old female presented with persistent and debilitating low back and leg pain limiting her function and quality of life. Standing scoliosis radiographs demonstrated adult degenerative scoliosis (ADS), with a lumbar scoliosis of 53°, a pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch of 44°, and pelvic tilt of 39°. Robotics planning software was utilized for preoperative planning of the multiple rod and 4-point pelvic fixation in the posterior construct.
Lessons: To the authors' knowledge, this is the first report detailing the use of spinal robotics for complex 11-level minimally invasive correction of ADS. Although additional experiences adapting spinal robotics to complex spinal deformities are necessary, the present case represents a proof-of-concept demonstrating the feasibility of applying this technology to minimally invasive correction of ASD.
Keywords: ASD; adult degenerative scoliosis; adult spinal deformity; minimally invasive; minimally invasive surgery; robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Minimally invasive multiple-rod constructs with robotics planning in adult spinal deformity surgery: a case series.Eur Spine J. 2022 Jan;31(1):95-103. doi: 10.1007/s00586-021-06980-4. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 34599407
-
Preoperative Robotics Planning Facilitates Complex Construct Design in Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery-A Preliminary Experience.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 22;13(7):1829. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071829. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610594 Free PMC article.
-
"Push-Through" Rod Passage Technique for the Improvement of Lumbar Lordosis and Sagittal Balance in Minimally Invasive Adult Degenerative Scoliosis Surgery.Clin Spine Surg. 2016 Oct;29(8):323-30. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000094. Clin Spine Surg. 2016. PMID: 25140537
-
Two- and three-year outcomes of minimally invasive and hybrid correction of adult spinal deformity.J Neurosurg Spine. 2021 Nov 5;36(4):595-608. doi: 10.3171/2021.7.SPINE21138. Print 2022 Apr 1. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021. PMID: 34740175 Review.
-
Minimally invasive versus open surgery for the correction of adult degenerative scoliosis: a systematic review.Neurosurg Rev. 2021 Apr;44(2):659-668. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01280-9. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Neurosurg Rev. 2021. PMID: 32166508
Cited by
-
Endoscopic Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Spine J. 2023 Dec;17(6):1139-1154. doi: 10.31616/asj.2023.0135. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Asian Spine J. 2023. PMID: 38105638 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal Robotics in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: Key Concepts and Technical Considerations.Asian J Neurosurg. 2025 Mar 31;20(3):448-455. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1806858. eCollection 2025 Sep. Asian J Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40852078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal Robotics in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Systematic Review.Neurospine. 2024 Mar;21(1):20-29. doi: 10.14245/ns.2347138.569. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Neurospine. 2024. PMID: 38317548 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Fractional Curve for Proper Management of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis.Neurospine. 2024 Jun;21(2):458-473. doi: 10.14245/ns.2347202.601. Epub 2024 Jun 30. Neurospine. 2024. PMID: 38955524 Free PMC article.
-
Oblique anterior column realignment with a mini-open posterior column osteotomy for minimally invasive adult spinal deformity correction: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Mar 11;7(11):CASE23680. doi: 10.3171/CASE23680. Print 2024 Mar 11. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 38467047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diebo BG, Shah NV, Boachie-Adjei O, et al. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):160–172. - PubMed
-
- Park P, Wang MY, Lafage V, et al. Comparison of two minimally invasive surgery strategies to treat adult spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(4):374–380. - PubMed
-
- Chan AK, Eastlack RK, Fessler RG, et al. Two- and three-year outcomes of minimally invasive and hybrid correction of adult spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021;36(4):595–608. - PubMed
-
- Chou D, Lafage V, Chan AY, et al. Patient outcomes after circumferential minimally invasive surgery compared with those of open correction for adult spinal deformity: initial analysis of prospectively collected data. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021;36(2):203–214. - PubMed
-
- Anand N, Kong C, Fessler RG. A staged protocol for circumferential minimally invasive surgical correction of adult spinal deformity. Neurosurgery. 2017;81(5):733–739. - PubMed

