The p97/VCP segregase is essential for arsenic-induced degradation of PML and PML-RARA
- PMID: 36880596
- PMCID: PMC10005898
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202201027
The p97/VCP segregase is essential for arsenic-induced degradation of PML and PML-RARA
Abstract
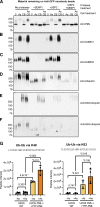
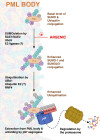
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia is caused by expression of the oncogenic Promyelocytic Leukemia (PML)-Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha (RARA) fusion protein. Therapy with arsenic trioxide results in degradation of PML-RARA and PML and cures the disease. Modification of PML and PML-RARA with SUMO and ubiquitin precedes ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. To identify additional components of this pathway, we performed proteomics on PML bodies. This revealed that association of p97/VCP segregase with PML bodies is increased after arsenic treatment. Pharmacological inhibition of p97 altered the number, morphology, and size of PML bodies, accumulated SUMO and ubiquitin modified PML and blocked arsenic-induced degradation of PML-RARA and PML. p97 localized to PML bodies in response to arsenic, and siRNA-mediated depletion showed that p97 cofactors UFD1 and NPLOC4 were critical for PML degradation. Thus, the UFD1-NPLOC4-p97 segregase complex is required to extract poly-ubiquitinated, poly-SUMOylated PML from PML bodies, prior to degradation by the proteasome.
© 2023 Jaffray et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Anderson, D.J., Le Moigne R., Djakovic S., Kumar B., Rice J., Wong S., Wang J., Yao B., Valle E., Kiss von Soly S., et al. 2015. Targeting the AAA ATPase p97 as an approach to treat cancer through disruption of protein homeostasis. Cancer Cell. 28:653–665. 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.10.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

