Six-Year Survival Outcomes for Patients with HER2-Positive Early Breast Cancer Treated with CT-P6 or Reference Trastuzumab: Observational Follow-Up Study of a Phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36881323
- PMCID: PMC10195725
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-023-00582-w
Six-Year Survival Outcomes for Patients with HER2-Positive Early Breast Cancer Treated with CT-P6 or Reference Trastuzumab: Observational Follow-Up Study of a Phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: The Phase 3 CT-P6 3.2 study demonstrated equivalent efficacy and comparable safety between CT-P6 and reference trastuzumab in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-positive early breast cancer after up to 3 years' follow-up.
Objective: To investigate long-term survival with CT-P6 and reference trastuzumab.
Methods: In the CT-P6 3.2 study, patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer were randomised to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with CT-P6 or reference trastuzumab, surgery, and adjuvant CT-P6 or reference trastuzumab before a 3-year post-treatment follow-up. Patients who completed the study could enter a 3-year extension (CT-P6 4.2 study). Data were collected every 6 months to assess overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and progression-free survival (PFS).
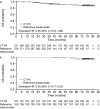
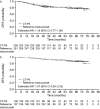
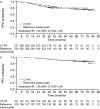
Results: Of 549 patients enrolled in the CT-P6 3.2 study, 216 (39.3%) patients continued in the CT-P6 4.2 study (CT-P6, 107; reference trastuzumab, 109) (intention-to-treat extension set). Median follow-up was 76.4 months for both groups. Medians were not reached for time-to-event parameters; estimated hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) for CT-P6 versus reference trastuzumab were 0.59 (0.17-2.02) for OS, 1.07 (0.50-2.32) for DFS, and 1.08 (0.50-2.34) for PFS. Corresponding 6-year survival rates in the CT-P6 and reference trastuzumab groups, respectively, were 0.96 (0.90-0.99) and 0.94 (0.87-0.97), 0.87 (0.78-0.92) and 0.89 (0.81-0.94), and 0.87 (0.78-0.92) and 0.89 (0.82-0.94).
Conclusions: Data from this extended follow-up of the CT-P6 3.2 study demonstrate the comparable long-term efficacy of CT-P6 and reference trastuzumab up to 6 years.
Eudract number: 2019-003518-15 (retrospectively registered 10 March 2020).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Justin Stebbing has received consulting fees or honoraria (2020–present) from Agenus, Alveo Technologies, APIM Therapeutics, Benevolent AI, Bryologyx, Celltrion, Certis, Eli Lilly, Equilibre Biopharmaceuticals, Graviton Bioscience Corporation, Greenmantle, Heat Biologics, IO Labs, Onconox, Pear Bio, Vaccitech, Volvox, vTv Therapeutics, and Zephyr AI; he has consulted with Lansdowne Partners and Vitruvian; he chairs the Board of Directors for Xerion and previously BB Biotech Healthcare Trust PLC; and is Editor-in-Chief of
Figures

References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Herzuma: prescribing information. 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/761091s001s002.... Accessed 6 Jan 2023.
-
- European Medicines Agency. Herzuma: summary of product characteristics. 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/herzuma-epar-.... Accessed 6 Jan 2023.
-
- Stebbing J, Baranau Y, Baryash V, Manikhas A, Moiseyenko V, Dzagnidze G, et al. CT-P6 compared with reference trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer: a randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 equivalence trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(7):917–928. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30434-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Esteva FJ, Baranau YV, Baryash V, Manikhas A, Moiseyenko V, Dzagnidze G, et al. Efficacy and safety of CT-P6 versus reference trastuzumab in HER2-positive early breast cancer: updated results of a randomised phase 3 trial. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019;84(4):839–847. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03920-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stebbing J, Baranau YV, Baryash V, Manikhas A, Moiseyenko V, Dzagnidze G, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of CT-P6 versus trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: final results from a randomized phase III trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021;188(3):631–640. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06240-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

