miR-27a-3p relieves heat stress-induced mitochondrial damage and aberrant milk protein synthesis through MEK/ERK pathway in BMECs
- PMID: 36881375
- PMCID: PMC10167065
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-023-01334-z
miR-27a-3p relieves heat stress-induced mitochondrial damage and aberrant milk protein synthesis through MEK/ERK pathway in BMECs
Abstract
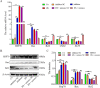
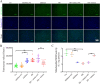
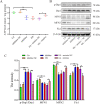
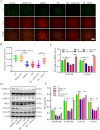
With global warming, heat stress has become a primary factor that compromises the health and milk quality of dairy cows. Here, we investigated the function and underlying regulatory mechanism of miR-27a-3p in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs) under heat-stress conditions. The current study showed that miR-27a-3p could prevent heat stress-induced BMEC oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage by regulating the balance between mitochondrial fission and fusion processes. Importantly, we found that miR-27a-3p could increase cell proliferation under heat stress conditions by regulating the MEK/ERK pathway and cyclin D1/E1. Interestingly, miR-27a-3p is also involved in the regulation of milk protein synthesis-related protein expression, such as CSN2 and ELF5. Inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway by AZD6244 blocked the regulatory function of miR-27a-3p in cell proliferation and milk protein synthesis in BMECs under heat stress conditions. Our findings demonstrated that miR-27a-3p protects BMECs from heat stress-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage through the MEK/ERK pathway, thereby promoting BMECs proliferation and lactation in dairy cows. The potential regulatory mechanism of miR-27a-3p in attenuating heat stress-induced apoptosis and lactation defect in BMECs.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; Lactation; MEK/ERK signaling pathway; Mitochondrial damage; miR-27a-3p.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Cell Stress Society International.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

