Integrating Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics to Explore the Effects of Dangshen (Codonopsis pilosula) Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Validation Based on the Active Compound Luteolin
- PMID: 36883114
- PMCID: PMC9985903
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S386941
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics to Explore the Effects of Dangshen (Codonopsis pilosula) Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Validation Based on the Active Compound Luteolin
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the pharmacological mechanism of Dangshen (Codonopsis pilosula) against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics, and to verify the anticancer effect of luteolin, the active ingredient of Codonopsis pilosula, on HCC cells.
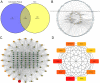
Methods: The effective compounds and potential targets of Codonopsis pilosula were established using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) database. The genes related to HCC were obtained through the GeneCards database. The interactive genes were imported into the Visualization and Integrated Discovery database for Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signal enrichment, and the hub genes were screened out. The Cancer Genome Atlas database was used to construct a prognosis model, and the prognosis and clinicopathological correlation were analyzed. In in vitro experiments, we verified the effects of luteolin, an active compound of Codonopsis pilosula, on the proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis and migration of HCC cells.
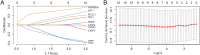
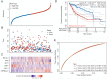
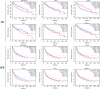
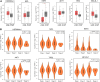
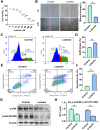
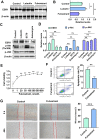
Results: A total of 21 effective compounds of Codonopsis pilosula and 98 potential downstream target genes were screened through the TCMSP database, and 1406 HCC target genes were obtained through the GeneCards database. Finally, 53 interacting genes between the two databases were obtained, among which, the 10 key node genes were CASP3, TP53, MDM2, AKT1, ESR1, BCL2L1, MCL1, HSP90AA1, CASP9, and CCND1, involving 77 typical GO terms and 72 KEGG signals. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve of the model group showed that the overall survival of the low-risk group was significantly higher than that of the high-risk group. Luteolin significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of HCC cells, induced apoptosis, and increased the G2/M phase ratio. Mechanistically, luteolin significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of MAPK-JNK and Akt (Thr308) and subsequently led to upregulation of ESR1. Pharmacological inhibition of ESR1 with fulvestrant enhanced cell viability and migration and attenuated apoptosis.
Conclusion: Codonopsis pilosula has potential for clinical development due to its anti-HCC properties. Luteolin, the effective component of Codonopsis pilosula, plays anti-HCC role through AKT- or MAPK-JNK signaling mediated ESR1.
Keywords: Codonopsis pilosula; bioinformatics; hepatocellular carcinoma; luteolin; network pharmacology.
© 2023 Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review of the Phytochemical Profile and Potential Medicinal Functions of Codonopsis pilosula in Cancer.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 24;13(3):e70054. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70054. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40008240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Codonopsis pilosula in inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155338. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155338. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38520835
-
The mechanistic study of codonopsis pilosula on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and experimental validation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1542116. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542116. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40351428 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology reveals the mechanism of the herbal pairing of Codonopsis Pilosula (Franch.) Nannf and Astragalus Membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge on chronic heart failure.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):7942-7959. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1469. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353081
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Network toxicology and molecular docking to investigative the non-acetylcholinesterase mechanisms and targets of cardiotoxicity injury induced by organophosphorus pesticides.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e39963. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039963. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465796 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of the Phytochemical Profile and Potential Medicinal Functions of Codonopsis pilosula in Cancer.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Feb 24;13(3):e70054. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70054. eCollection 2025 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40008240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine in acute mountain sickness: pathogenesis, mechanisms and future directions.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1393209. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1393209. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38895636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network pharmacology and bioinformatic integrative analysis reveals candidate gene targets and potential therapeutic of East Kalimantan propolis against hepatocellular carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 19;10(21):e39142. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39142. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524833 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated network pharmacology and transcriptomics to explore the mechanism of compound Dihuang granule (CDG) protects dopaminergic neurons by regulating the Nrf2/HMOX1 pathway in the 6-OHDA/MPP+-induced model of Parkinson's disease.Chin Med. 2024 Dec 18;19(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01040-7. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39696456 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

