Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: a phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 36883141
- PMCID: PMC9981330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101889
Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: a phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: An urgent need exists to rapidly screen potential therapeutics for severe COVID-19 or other emerging pathogens associated with high morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Using an adaptive platform design created to rapidly evaluate investigational agents, hospitalised patients with severe COVID-19 requiring ≥6 L/min oxygen were randomised to either a backbone regimen of dexamethasone and remdesivir alone (controls) or backbone plus one open-label investigational agent. Patients were enrolled to the arms described between July 30, 2020 and June 11, 2021 in 20 medical centres in the United States. The platform contained up to four potentially available investigational agents and controls available for randomisation during a single time-period. The two primary endpoints were time-to-recovery (<6 L/min oxygen for two consecutive days) and mortality. Data were evaluated biweekly in comparison to pre-specified criteria for graduation (i.e., likely efficacy), futility, and safety, with an adaptive sample size of 40-125 individuals per agent and a Bayesian analytical approach. Criteria were designed to achieve rapid screening of agents and to identify large benefit signals. Concurrently enrolled controls were used for all analyses. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04488081.
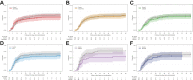
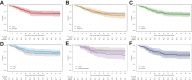
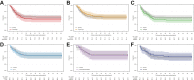
Findings: The first 7 agents evaluated were cenicriviroc (CCR2/5 antagonist; n = 92), icatibant (bradykinin antagonist; n = 96), apremilast (PDE4 inhibitor; n = 67), celecoxib/famotidine (COX2/histamine blockade; n = 30), IC14 (anti-CD14; n = 67), dornase alfa (inhaled DNase; n = 39) and razuprotafib (Tie2 agonist; n = 22). Razuprotafib was dropped from the trial due to feasibility issues. In the modified intention-to-treat analyses, no agent met pre-specified efficacy/graduation endpoints with posterior probabilities for the hazard ratios [HRs] for recovery ≤1.5 between 0.99 and 1.00. The data monitoring committee stopped Celecoxib/Famotidine for potential harm (median posterior HR for recovery 0.5, 95% credible interval [CrI] 0.28-0.90; median posterior HR for death 1.67, 95% CrI 0.79-3.58).
Interpretation: None of the first 7 agents to enter the trial met the prespecified criteria for a large efficacy signal. Celecoxib/Famotidine was stopped early for potential harm. Adaptive platform trials may provide a useful approach to rapidly screen multiple agents during a pandemic.
Funding: Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative is the trial sponsor. Funding for this trial has come from: the COVID R&D Consortium, Allergan, Amgen Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Implicit Bioscience, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc., Roche/Genentech, Apotex Inc., FAST Grant from Emergent Venture George Mason University, The DoD Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA), The Department of Health and Human ServicesBiomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), and The Grove Foundation. Effort sponsored by the U.S. Government under Other Transaction number W15QKN-16-9-1002 between the MCDC, and the Government.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Clinical trial; Respiratory insufficiency; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023 The Author.
Conflict of interest statement
NA reports institutional research funding from the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA), and the Department of HHS Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA); reports grants from the National Institute of Health (NIH); and reports honoraria from Young Investigators Respiratory Disease Forum. JRB reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative and the National Institute of Health (NIH); reports payment or honoraria from Sedana Medical, Hamilton Medical, and BioMarck Pharmaceuticals; and serves as an associate editor of Critical Care. PB serves as a contracted consulted for Auris Health and Johnson & Johnson; and reports payment for expert testimony from University of Minnesota Physicians Group. EB reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative. CSC reports grants or institutional funding from the National Institute of Health (NIH), Roche-Genenetch, and Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative; and reports consulting feed from Cellenkos, Vasomune, Gen1e Life Sciences, and NGM Bio. LE is an unpaid Board Member at Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative. DCF reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative and the National Institute of Health (NIH); reports consulting fees from Cytovale; and reports participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Medpace. SG reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative; reports participation on a Scientific Advisory Board and holds stock in Respana Therapeutics. KDL reports institutional research funding from the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA), and the Department of HHS Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA). TRM reports consulting fees from Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. MM reports consulting fees from Gilead Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Citius Pharmaceuticals, and Pliant Therapeutics; and reports institutional funding from Roche Genentech, the Department of Defense, Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative, Regenerative Medicine, the National Institute of Health (NIH), the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. NJM reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative and the Marcus Foundation; reports grants from the National Institute of Health (HL137006, HL137915, HL155804, GM115553), and BioMarch Inc. (BIO-11006); reports honoraria from University of Pittsburgh, Department of Critical Care Grand Rounds, and NYU Langone Pulmonary Critical Care Grand Rounds, Brown University Investigators in Respiratory Diseases, ViralED and Penn Center for AIDS Research, and University of Colorado Pulmonary Research Excellence Conference; reports travel support from the Aspen Lung Conference; and reports participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for the Careful Ventilation in ARDS Trial (CAVIARDS), and NHLBI Observational Study Monitoring Board for SPIROMICS II. DWR reports institutional research funding from the National Institute of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative; reports travel support from the National Institute of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, and Department of Veteran's Affairs; and holds stock in Achieve Life Sciences. KWT reports royalties from UpToDate; reports payment for expert testimony from Bencoe & Lacour Law PC, and Jakeway Injury Law; and holds stock in Johnson & Johnson, Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myer Squibb, Pfizer, and Doximity. AR reports grant from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (T32HS026121). KWG reports grants from the National Institute of Health (ACTIV4-HT/NECTAR, NEXIS-FLAME R32). JPR reports institutional research funding from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative and the National Institute of Health (HL155159). JD reports grant funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (T32HL116271). GRSB reports grant funding from the National Institute of Health and the Veterans Administration. BDS reports grants from the National Institute of Health (R01HL149883, R01HL153122, P01HL154998, P01AG049665, U19AI135964); reports participating in an Advisory Board, and owns stock in Zoe Biosciences; and reports patent, “Compositions and Methods to Accelerate Resolution of Acute Lung Inflammation,” (US 10, 905, 706 B2). JL reports personal fees from Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative for serving as Chair of the Safety Working Group for the ISPY COVID Trial. PH and ID are full time employees of Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Woodcock J., Araojo R., Thompson T., Puckrein G.A. Integrating research into community practice - toward increased diversity in clinical trials. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(15):1351–1353. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths G., Fitzgerald R., Jaki T., et al. AGILE-ACCORD: a randomized, multicentre, seamless, adaptive phase I/II platform study to determine the optimal dose, safety and efficacy of multiple candidate agents for the treatment of COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised platform trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):544. - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

