Evaluation of right ventricular strain in two separate cohorts with precapillary pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 36883189
- PMCID: PMC9985931
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12204
Evaluation of right ventricular strain in two separate cohorts with precapillary pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
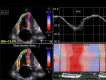
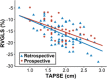
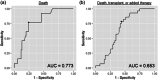
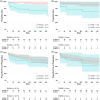
Evaluation for right ventricular (RV) dysfunction is an important part of risk assessment in care of patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) as it is associated with morbidity and mortality. Echocardiography provides a widely available and acceptable method to assess RV function. RV global longitudinal strain (RVGLS), a measure of longitudinal shortening of RV deep muscle fibers obtained by two-dimensional echocardiography, was previously shown to predict short-term mortality in patients with PH. The purpose of the current study was to assess the performance of RVGLS in predicting 1-year outcomes in PH. We retrospectively identified 83 subjects with precapillary PH and then enrolled 50 consecutive prevalent pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) subjects into a prospective validation cohort. Death as well as combined morbidity and mortality events at 1 year were assessed as outcomes. In the retrospective cohort, 84% of patients had PAH and the overall 1-year mortality rate was 16%. Less negative RVGLS was marginally better than tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) as a predictor for death. However, in the prospective cohort, 1-year mortality was only 2%, and RVGLS was not predictive of death or a combined morbidity and mortality outcome. This study supports that RV strain and TAPSE have similar 1-year outcome predictions but highlights that low TAPSE or less negative RV strain measures are often false-positive in a cohort with low baseline mortality risk. While RV failure is considered the final common pathway for disease progression in PAH, echocardiographic measures of RV function may be less informative of risk in serial follow-up of treated PAH patients.
Keywords: clinical studies; echocardiography; mortality/survival; prognosis; pulmonary hypertension.
© 2023 The Authors. Pulmonary Circulation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Echocardiographic right ventricular strain from multiple apical views is superior for assessment of right ventricular systolic function.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2019 Mar;39(2):168-176. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12552. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30375714
-
Accuracy of echocardiographic indices for serial monitoring of right ventricular systolic function in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 9;12(11):e0187806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187806. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29121072 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Assessment of Right Ventricular Function and Response to Therapy in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Oct 15;124(8):1298-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.07.026. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31481176
-
Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion (TAPSE) for Risk Stratification and Prognostication of Patients with Pulmonary Embolism.J Emerg Med. 2020 Mar;58(3):449-456. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Nov 15. J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 31735658 Review.
-
The Predictive Value of Right Ventricular Longitudinal Strain in Pulmonary Hypertension, Heart Failure, and Valvular Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 17;8:698158. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.698158. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34222387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring of the right ventricular responses to pressure overload: prognostic value and usefulness of echocardiography for clinical decision-making.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024 Feb 15;14(1):193-222. doi: 10.21037/cdt-23-380. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38434557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress of right ventricular strain imaging evaluation technology in pulmonary arterial hypertension].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 15;26(8):887-892. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2403071. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39148396 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Humbert M, Guignabert C, Bonnet S, Dorfmüller P, Klinger JR, Nicolls MR, Olschewski AJ, Pullamsetti SS, Schermuly RT, Stenmark KR, Rabinovitch M. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: state of the art and research perspectives. Eur Respir J. 2019;53:1801887. 10.1183/13993003.01887-2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forfia PR, Fisher MR, Mathai SC, Housten‐Harris T, Hemnes AR, Borlaug BA, Chamera E, Corretti MC, Champion HC, Abraham TP, Girgis RE, Hassoun PM. Tricuspid annular displacement predicts survival in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174:1034–41. 10.1164/rccm.200604-547OC - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghio S, Guazzi M, Scardovi AB, Klersy C, Clemenza F, Carluccio E, Temporelli PL, Rossi A, Faggiano P, Traversi E, Vriz O, Dini FL. Different correlates but similar prognostic implications for right ventricular dysfunction in heart failure patients with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19:873–9. 10.1002/ejhf.664 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

