Functional analysis of protein post-translational modifications using genetic codon expansion
- PMID: 36883310
- PMCID: PMC10031814
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4618
Functional analysis of protein post-translational modifications using genetic codon expansion
Abstract
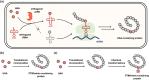
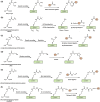
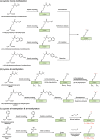
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins not only exponentially increase the diversity of proteoforms, but also contribute to dynamically modulating the localization, stability, activity, and interaction of proteins. Understanding the biological consequences and functions of specific PTMs has been challenging for many reasons, including the dynamic nature of many PTMs and the technical limitations to access homogenously modified proteins. The genetic code expansion technology has emerged to provide unique approaches for studying PTMs. Through site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids (UAAs) bearing PTMs or their mimics into proteins, genetic code expansion allows the generation of homogenous proteins with site-specific modifications and atomic resolution both in vitro and in vivo. With this technology, various PTMs and mimics have been precisely introduced into proteins. In this review, we summarize the UAAs and approaches that have been recently developed to site-specifically install PTMs and their mimics into proteins for functional studies of PTMs.
Keywords: bioorthogonal reaction; genetic codon expansion; post-translational modification; unnatural amino acids.
© 2023 The Protein Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expanding horizons: genetic code expansion technology in the study of PTM functions.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Feb 1;118:118049. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.118049. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39729921 Review.
-
Applications of Genetic Code Expansion in Studying Protein Post-translational Modification.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 30;434(8):167424. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167424. Epub 2021 Dec 28. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34971673 Review.
-
Chemogenetic and optogenetic control of post-translational modifications through genetic code expansion.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021 Aug;63:123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.02.016. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33845403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Strategies for Probing the Biological Functions of Protein Post-translational Modifications in Mammalian Cells with Genetic Code Expansion.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Oct 17;56(20):2827-2837. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00460. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37793174
-
Investigation of protein post-translational modifications with site-specifically incorporated non-canonical amino acids.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Jan 1;117:118013. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.118013. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39602864 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the prognostic role and expression patterns of FAM3A family genes in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05658-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594565 Free PMC article.
-
Computationally Assisted Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):84-90. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c01544. eCollection 2025 Jan 22. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39866708 Free PMC article.
-
Nonenzymatic lysine D-lactylation induced by glyoxalase II substrate SLG dampens inflammatory immune responses.Cell Res. 2025 Feb;35(2):97-116. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-01060-w. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 39757301 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging regulatory mechanisms and functions of biomolecular condensates: implications for therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 6;10(1):4. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02070-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39757214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations of Key Functional Residues in CRM1/XPO1 Differently Alter Its Intranuclear Localization and the Nuclear Export of Endogenous Cargos.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 10;14(12):1578. doi: 10.3390/biom14121578. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akahoshi A, Suzue Y, Kitamatsu M, Sisido M, Ohtsuki T. Site‐specific incorporation of arginine analogs into proteins using arginyl‐tRNA synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414(3):625–30. - PubMed
-
- Alfonta L, Zhang Z, Uryu S, Loo JA, Schultz PG. Site‐specific incorporation of a redox‐active amino acid into proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(48):14662–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

