Directed Biosynthesis of Mitragynine Stereoisomers
- PMID: 36883326
- PMCID: PMC9999412
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c13644
Directed Biosynthesis of Mitragynine Stereoisomers
Abstract
Mitragyna speciosa ("kratom") is used as a natural remedy for pain and management of opioid dependence. The pharmacological properties of kratom have been linked to a complex mixture of monoterpene indole alkaloids, most notably mitragynine. Here, we report the central biosynthetic steps responsible for the scaffold formation of mitragynine and related corynanthe-type alkaloids. We illuminate the mechanistic basis by which the key stereogenic center of this scaffold is formed. These discoveries were leveraged for the enzymatic production of mitragynine, the C-20 epimer speciogynine, and fluorinated analogues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

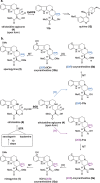


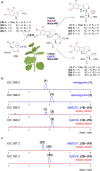
References
-
- Cinosi E.; Martinotti G.; Simonato P.; Singh D.; Demetrovics Z.; Roman-Urrestarazu A.; Bersani F. S.; Vicknasingam B.; Piazzon G.; Li J.-H.; Yu W.-J.; Kapitány-Fövény M.; Farkas J.; Di Giannantonio M.; Corazza O. Following “the Roots” of Kratom (Mitragyna Speciosa): The Evolution of an Enhancer from a Traditional Use to Increase Work and Productivity in Southeast Asia to a Recreational Psychoactive Drug in Western Countries. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. 10.1155/2015/968786. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

