The DZHK research platform: maximisation of scientific value by enabling access to health data and biological samples collected in cardiovascular clinical studies
- PMID: 36884078
- PMCID: PMC10293401
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-023-02177-5
The DZHK research platform: maximisation of scientific value by enabling access to health data and biological samples collected in cardiovascular clinical studies
Abstract
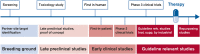
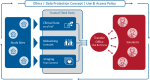
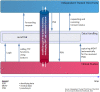
The German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) is one of the German Centres for Health Research and aims to conduct early and guideline-relevant studies to develop new therapies and diagnostics that impact the lives of people with cardiovascular disease. Therefore, DZHK members designed a collaboratively organised and integrated research platform connecting all sites and partners. The overarching objectives of the research platform are the standardisation of prospective data and biological sample collections among all studies and the development of a sustainable centrally standardised storage in compliance with general legal regulations and the FAIR principles. The main elements of the DZHK infrastructure are web-based and central units for data management, LIMS, IDMS, and transfer office, embedded in a framework consisting of the DZHK Use and Access Policy, and the Ethics and Data Protection Concept. This framework is characterised by a modular design allowing a high standardisation across all studies. For studies that require even tighter criteria additional quality levels are defined. In addition, the Public Open Data strategy is an important focus of DZHK. The DZHK operates as one legal entity holding all rights of data and biological sample usage, according to the DZHK Use and Access Policy. All DZHK studies collect a basic set of data and biosamples, accompanied by specific clinical and imaging data and biobanking. The DZHK infrastructure was constructed by scientists with the focus on the needs of scientists conducting clinical studies. Through this, the DZHK enables the interdisciplinary and multiple use of data and biological samples by scientists inside and outside the DZHK. So far, 27 DZHK studies recruited well over 11,200 participants suffering from major cardiovascular disorders such as myocardial infarction or heart failure. Currently, data and samples of five DZHK studies of the DZHK Heart Bank can be applied for.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Data and biomaterial collection; German Centre for Cardiovascular Research; Research platform; Standardisation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- German Centre for Cardiovascular Research. Available from: https://dzhk.de/en/. Accessed 12 Dec 2022.
-
- BMBF Initiative “German Centres for Health Research”. Available from: https://dzhk.de/das-dzhk/kooperationen/deutsche-zentren-der-gesundheitsf.... Accessed 12 Dec 2022.
-
- German Centre for Cardiocascular Research, Internal Study Centres. Available from: https://dzhk.de/en/research/clinical-research/internal-study-centres/. Accessed 12 Dec 2022.
-
- German Centre for Cardiovascular Research, Focus on Translation. Available from: https://dzhk.de/en/research/research-focus/focus-on-translation/. Accessed 12 Dec 2022.
-
- Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, Blomberg N, Boiten JW, da Silva Santos LB, Bourne PE, Bouwman J, Brookes AJ, Clark T, Crosas M, Dillo I, Dumon O, Edmunds S, Evelo CT, Finkers R, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Gray AJ, Groth P, Goble C, Grethe JS, Heringa J, Hoen TPA, Hooft R, Kuhn T, Kok R, Kok J, Lusher SJ, Martone ME, Mons A, Packer AL, Persson B, Rocca-Serra P, Roos M, van Schaik R, Sansone SA, Schultes E, Sengstag T, Slater T, Strawn G, Swertz MA, Thompson M, van der Lei J, van Mulligen E, Velterop J, Waagmeester A, Wittenburg P, Wolstencroft K, Zhao J, Mons B. The FAIR guiding principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci Data. 2016;3:160018. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

