Purification, characterization, and enzyme kinetics of a glutathione S transferase from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii
- PMID: 36884105
- PMCID: PMC9995618
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-023-00486-w
Purification, characterization, and enzyme kinetics of a glutathione S transferase from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii
Abstract
Background: Glutathione s-transferases (GSTs) perform an essential role in detoxification of xenobiotics and endogenous compounds via their conjugation to reduce glutathione.
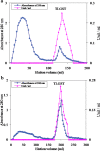
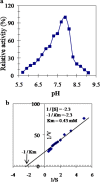
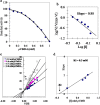
Results: A GST enzyme, designated tick larvae glutathione S transferase (TLGST), was purified from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii via ammonium sulfate precipitation, glutathione-Sepharose affinity column and Sephacryl S-300 chromatography. TLGST-specific activity was found to be 1.56 Umg-1 which represents 39 folds and 32.2% recovery. The molecular weight of TLGST purified from camel tick larvae was found as 42 kDa by gel filtration. TLGST has a pI value of 6.9 and was found a heterodimeric protein of 28 and 14 kDa subunits as detected on SDS-PAGE. The Lineweaver-Burk plot calculated the km for CDNB to be 0.43 mM with Vmax value of 9.2 Umg-1. TLGST exhibited its optimal activity at pH 7.9. Co2+, Ni2+ and Mn2+ increased the activity of TLGST while Ca2+, Cu2+, Fe2+ and Zn2+ inhibited it. TLGST was inhibited by cumene hydroperoxide, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, lithocholic acid, hematin, triphenyltin chloride, p-chloromercuribenzoic acid (pCMB), N-p-Tosyl-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone (TPCK), iodoacetamide, EDTA and quercetin. pCMB inhibited TLGST competitively with Ki value of 0.3 mM.
Conclusions: These findings will help to understand the various physiologic conditions of ticks and targeting TLGST could be significant tool for development of prospective vaccines against ticks as a bio-control strategy to overcome the rapid grows in pesticide-resistant tick populations.
Keywords: Camel tick; Characterization; Glutathione-S-transferase; Hyalomma dromedarii; Purification.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Catalase from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015 Oct 22;4:411-416. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.09.023. eCollection 2015 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015. PMID: 29124232 Free PMC article.
-
Apyrase with anti-platelet aggregation activity from the nymph of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii.Exp Appl Acarol. 2020 Mar;80(3):349-361. doi: 10.1007/s10493-020-00471-9. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Exp Appl Acarol. 2020. PMID: 31927645
-
Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of a functional GSTmu class from the cattle tick Boophilus annulatus.Vet Parasitol. 2008 Mar 25;152(1-2):116-26. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.12.014. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Vet Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18241993
-
alpha-Amylase from developing embryos of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 May;126(1):99-108. doi: 10.1016/s0305-0491(00)00165-6. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10825669
-
Superoxide dismutases from larvae of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Mar;164(3):221-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23333534
References
-
- Adewale IO, Afolayan A. Studies on glutathione transferase from grasshopper (Zonocerus variegatus) Pestic Biochem Phys. 2006;85:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2005.10.004. - DOI
-
- Alanazi AD, Nguyen VL, Alyousif MS, Manoj RRS, Alouffi AS, Donato R, Sazmand A, Mendoza-Roldan JA, Dantas-Torres F, Otranto D. Ticks and associated pathogens in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Riyadh Province. Saudi Arabia Parasit Vector. 2020;13(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-3973-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balc N, Turkan F, Sakiroglu H, Aygun A, Sen F. Purification and characterization of glutathione S-transferase from blueberry fruits (Vaccinium arctostaphylos L.) and investigated of some pesticide inhibition effects on enzyme activity. Heliyon. 2019;5:e01422. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
