Potential antiviral activities of chrysin against hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 36895013
- PMCID: PMC9995728
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-023-00531-6
Potential antiviral activities of chrysin against hepatitis B virus
Abstract
Background: Interferon and nucleos(t)ide analogues are current therapeutic treatments for chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection with the limitations of a functional cure. Chrysin (5, 7-dihydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonoid, known for its antiviral and hepatoprotective activities. However, its anti-HBV activity is unexplored.
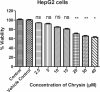
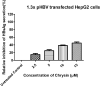
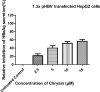
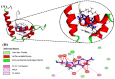
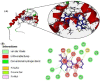
Methods: In the present study, the anti-hepatitis B activity of chrysin was investigated using the in vitro experimental cell culture model, HepG2 cells. In silico studies were performed where chrysin and lamivudine (used here as a positive control) were docked with high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1). For the in vitro studies, wild type HBV genome construct (pHBV 1.3X) was transiently transfected in HepG2. In culture supernatant samples, HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Secreted HBV DNA and intracellular covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) were measured by SYBR green real-time PCR. The 3D crystal structure of HMGB1 (1AAB) protein was developed and docked with the chrysin and lamivudine. In silico drug-likeness, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Toxicity (ADMET) properties of finest ligands were performed by using SwissADME and admetSAR web servers.
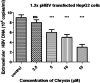
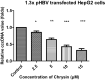
Results: Data showed that chrysin significantly decreases HBeAg, HBsAg secretion, supernatant HBV DNA and cccDNA, in a dose dependent manner. The docking studies demonstrated HMGB1 as an important target for chrysin as compared to lamivudine. Chrysin revealed high binding affinity and formed a firm kissing complex with HMGB1 (∆G = - 5.7 kcal/mol), as compared to lamivudine (∆G = - 4.3 kcal/mol), which might be responsible for its antiviral activity.
Conclusions: The outcome of our study establishes chrysin as a new antiviral against HBV infection. However, using chrysin to treat chronic HBV disease needs further endorsement and optimization by in vivo studies in animal models.
Keywords: CccDNA; Chrysin; HMGB1; Hepatitis B virus; In silico.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist in publishing this article.
Figures
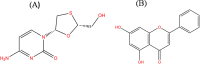
Similar articles
-
Reduction of hepatitis B surface antigen and covalently closed circular DNA by nucleos(t)ide analogues of different potency.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Aug;11(8):1004-10.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.01.026. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23376799
-
Serum Hepatitis B Virus DNA, RNA, and HBsAg: Which Correlated Better with Intrahepatic Covalently Closed Circular DNA before and after Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Treatment?J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Oct;55(10):2972-2982. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00760-17. Epub 2017 Jul 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28747369 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol. 2017 Feb;66(2):275-281. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27639844
-
Aiming for cure in HBV and HDV infection.J Hepatol. 2016 Oct;65(4):835-848. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.043. Epub 2016 Jun 3. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27270043 Review.
-
How to achieve functional cure of HBV: Stopping NUCs, adding interferon or new drug development?J Hepatol. 2022 Jun;76(6):1249-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.024. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35589248 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of Chrysin-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Decorated Niosomal Nanoparticles: Potential Anti-inflammatory and Anti-osteoclastic Effects on PBMCs of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Adv Pharm Bull. 2025 Jan 5;15(1):95-106. doi: 10.34172/apb.43185. eCollection 2025 Apr. Adv Pharm Bull. 2025. PMID: 40636298 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Antiviral Activity of Synthetic Compounds Against Mayaro Virus.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 13;18(5):717. doi: 10.3390/ph18050717. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430536 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of chrysin and naringenin against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Dec 7;10:1278997. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1278997. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38130439 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the immunological mechanisms in hepatitis B virus reactivation: Implications for disease progression and management strategies.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 14;30(10):1295-1312. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1295. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38596493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fung J. Prevention of hepatitis B virus recurrence. Hepat Res. 2021;7:33.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

