Prognostic value of genomic mutations in metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 36895385
- PMCID: PMC9988500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13827
Prognostic value of genomic mutations in metastatic prostate cancer
Abstract
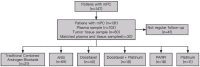
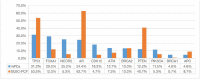
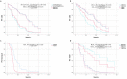
Metastatic prostate cancer (mPC) has a poor prognosis, and new treatment strategies are currently being offered for patients in clinical practice, but mPC is still incurable. A considerable proportion of patients with mPC harbor homologous recombination repair (HRR) mutations, which may be more sensitive to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPis). We retrospectively included genomic and clinical data from 147 patients with mPC from a single clinical center, with a total of 102 circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) samples and 60 tissue samples. The frequency of genomic mutations was analyzed and compared with that in Western cohorts. Cox analysis was used to assess progression-free survival (PFS) and prognostic factors related to prostate-specific antigen (PSA) after standard systemic therapy for mPC. The most frequently mutated gene in the HRR pathway was CDK12 (18.3%), followed by ATM (13.7%) and BRCA2 (13.0%). The remaining common ones were TP53 (31.3%), PTEN (12.2%), and PIK3CA (11.5%). The frequency of BRCA2 mutation was close to that of the SU2C-PCF cohort (13.3%), but the frequency of CDK12, ATM, and PIK3CA mutations was significantly higher than that in the SU2C-PCF cohort: 4.7%, 7.3%, and 5.3%, respectively. CDK12 mutation were less responsive to androgen receptor signaling inhibitors (ARSIs), docetaxel, and PARPi. BRCA2 mutation helps predict PARPi efficacy. Additionally, androgen receptor (AR)-amplified patients do not respond well to ARSIs, and PTEN mutation are associated with poorer docetaxel response. These findings support the genetic profiling of patients with mPC after diagnosis to guide treatment stratification to customize personalized treatment.
Keywords: Metastatic prostate cancer in china; Next generation sequencing; Prognosis; Somatic gene mutation.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Mottet N., et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur. Urol. 2017;71(4):618–629. - PubMed
-
- Cornford P., et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017;71(4):630–642. - PubMed
-
- Nuhn P., et al. Update on systemic prostate cancer therapies: management of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in the era of precision oncology. Eur. Urol. 2019;75(1):88–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

