Recent progress in cancer cell membrane-based nanoparticles for biomedical applications
- PMID: 36895440
- PMCID: PMC9989677
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.14.24
Recent progress in cancer cell membrane-based nanoparticles for biomedical applications
Abstract
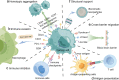
Immune clearance and insufficient targeting have limited the efficacy of existing therapeutic strategies for cancer. Toxic side effects and individual differences in response to treatment have further limited the benefits of clinical treatment for patients. Biomimetic cancer cell membrane-based nanotechnology has provided a new approach for biomedicine to overcome these obstacles. Biomimetic nanoparticles exhibit various effects (e.g., homotypic targeting, prolonging drug circulation, regulating the immune system, and penetrating biological barriers) after encapsulation by cancer cell membranes. The sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic methods will also be improved by utilizing the properties of cancer cell membranes. In this review, different properties and functions of cancer cell membranes are presented. Utilizing these advantages, nanoparticles can exhibit unique therapeutic capabilities in various types of diseases, such as solid tumors, hematological malignancies, immune system diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, cancer cell membrane-encapsulated nanoparticles show improved effectiveness and efficiency in combination with current diagnostic and therapeutic methods, which will contribute to the development of individualized treatments. This strategy has promising clinical translation prospects, and the associated challenges are discussed.
Keywords: cancer cell biomimetics; nanoparticles; precision medicine; targeted therapy; theranostic nanomedicine.
Copyright © 2023, Lin et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Acta Biomater. 2020 Aug;112:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 May 26. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32470527 Review.
-
Stem cell membrane, stem cell-derived exosomes and hybrid stem cell camouflaged nanoparticles: A promising biomimetic nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics.J Control Release. 2022 Aug;348:706-722. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.026. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35732250 Review.
-
Stem cell membrane-coated abiotic nanomaterials for biomedical applications.J Control Release. 2022 Nov;351:174-197. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.012. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36103910 Review.
-
Construction of Biomimetic-Responsive Nanocarriers and their Applications in Tumor Targeting.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(12):2255-2273. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220106105315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34994336
-
Biomimetic hybrid membrane-based nanoplatforms: synthesis, properties and biomedical applications.Nanoscale Horiz. 2020 Sep 1;5(9):1293-1302. doi: 10.1039/d0nh00267d. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020. PMID: 32608425 Review.
Cited by
-
Multistage Self-Assembled Nanomaterials for Cancer Immunotherapy.Molecules. 2023 Nov 24;28(23):7750. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237750. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent updates in applications of nanomedicine for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1105-1116. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.15.89. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39188757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carcinomembrane-Camouflaged Perfluorochemical Dual-Layer Nanopolymersomes Bearing Indocyanine Green and Camptothecin Effectuate Targeting Photochemotherapy of Cancer.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):6332-6343. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01150. Epub 2024 Sep 12. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 39264032 Free PMC article.
-
Application of nanomedicines in tumor immunotherapy.J Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jun 12;16(12):mjae055. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae055. J Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39730142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Parameters for Optimized Photoconversion Efficiency in Synergistic Cancer Treatment.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jul 25;15(8):207. doi: 10.3390/jfb15080207. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39194645 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
