Distinctive modulation of hepcidin in cancer and its therapeutic relevance
- PMID: 36895478
- PMCID: PMC9989193
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1141603
Distinctive modulation of hepcidin in cancer and its therapeutic relevance
Abstract
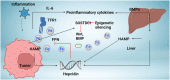
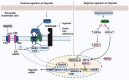
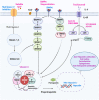
Hepcidin, a short peptide synthesized primarily by hepatocytes in response to increased body iron and inflammation, is a crucial iron-regulating factor. Hepcidin regulates intestinal iron absorption and releases iron from macrophages into plasma through a negative iron feedback mechanism. The discovery of hepcidin inspired a torrent of research into iron metabolism and related problems, which have radically altered our understanding of human diseases caused by an excess of iron, an iron deficiency, or an iron disparity. It is critical to decipher how tumor cells manage hepcidin expression for their metabolic requirements because iron is necessary for cell survival, particularly for highly active cells like tumor cells. Studies show that tumor and non-tumor cells express and control hepcidin differently. These variations should be explored to produce potential novel cancer treatments. The ability to regulate hepcidin expression to deprive cancer cells of iron may be a new weapon against cancer cells.
Keywords: cancer; hepcidin; homeostasis; iron; metabolism; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2023 Lin, Tuffour, Hao, Peprah, Huang, Zhou and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepcidin: a direct link between iron metabolism and immunity.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;37(9):1768-73. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.02.023. Epub 2005 Mar 16. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16009323 Review.
-
[Molecular mechanisms of iron homeostasis].Med Sci (Paris). 2004 Jan;20(1):68-72. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200420168. Med Sci (Paris). 2004. PMID: 14770366 Review. French.
-
[Iron metabolism: State of the art].Rev Med Interne. 2013 Jan;34(1):17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2012.04.006. Epub 2012 May 15. Rev Med Interne. 2013. PMID: 22595534 Review. French.
-
[Properties and advance of hepcidin].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006 May;22(3):361-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16755911 Review. Chinese.
-
Effect of hepcidin antagonists on anemia during inflammatory disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;226:107877. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107877. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33895185 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepcidin and Tissue-Specific Iron Regulatory Networks.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1480:89-102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-92033-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40603786 Review.
-
The Importance and Essentiality of Natural and Synthetic Chelators in Medicine: Increased Prospects for the Effective Treatment of Iron Overload and Iron Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4654. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094654. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Iron on Cancer-Related Immune Functions in Oncology: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 13;16(24):4156. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244156. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Metabolism in Cancer and Senescence: A Cellular Perspective.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jul 11;12(7):989. doi: 10.3390/biology12070989. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Hepcidin Levels in Breast Cancer Patients: Investigating the Correlation to Tumor Stage-A Cross-Sectional Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 10;8(8):e71148. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71148. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40791284 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

