Complementarity determining regions in SARS-CoV-2 hybrid immunity
- PMID: 36895570
- PMCID: PMC9990870
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1050037
Complementarity determining regions in SARS-CoV-2 hybrid immunity
Abstract
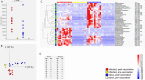
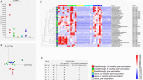
Pre-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection can boost protection elicited by COVID-19 vaccination and post-vaccination breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection can boost existing immunity conferred by COVID-19 vaccination. Such 'hybrid immunity' is effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants. In order to understand 'hybrid immunity' at the molecular level we studied the complementarity determining regions (CDR) of anti-RBD (receptor binding domain) antibodies isolated from individuals with 'hybrid immunity' as well as from 'naive' (not SARS-CoV-2 infected) vaccinated individuals. CDR analysis was done by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry-mass spectrometry. Principal component analysis and partial least square differential analysis showed that COVID-19 vaccinated people share CDR profiles and that pre-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection or breakthrough infection further shape the CDR profile, with a CDR profile in hybrid immunity that clustered away from the CDR profile in vaccinated people without infection. Thus, our results show a CDR profile in hybrid immunity that is distinct from the vaccination-induced CDR profile.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; complementary determining region; hybrid immunity; vaccination.
Copyright © 2023 Frans, Dillaerts, Dehaemers, Van Elslande, De Leeuw, Boon, Maes, Callewaert, Calcoen, Ancheva, Cockx, Geukens, Arat, Derua, Vermeersch, Carpentier and Bossuyt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cerqueira-Silva T, Andrews JR, Boaventura VS, Ranzani OT, de Araújo Oliveira V, Paixão ES, et al. . Effectiveness of CoronaVac, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, BNT162b2, and Ad26.COV2.S among individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection in Brazil: A test-negative, case-control study. Lancet Infect Dis (2022) 22:791–801. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00140-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

