The influence of age and sex on speed-strength performance in children between 10 and 14 years of age
- PMID: 36895629
- PMCID: PMC9989187
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1092874
The influence of age and sex on speed-strength performance in children between 10 and 14 years of age
Abstract
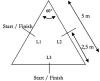
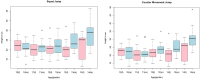
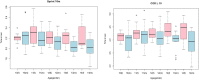
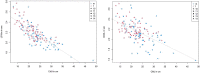
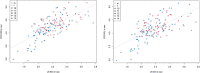
Introduction: Speed-strength performance is important during human movements such as jumping, sprinting, and change of direction (COD) tasks, which are a substantial part of sports practice. Sex and age seem to influence performance output in young persons; however, few studies have focused on the influence of sex and age measured via standard protocols of performance diagnostics. Method: Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the influence of age and sex on linear sprint (LS), COD sprint, countermovement jump (CMJ) height, squat-jump (SJ) height, and drop-jump (DJ) height performance in untrained children and adolescents via a cross-sectional analysis. This study comprised 141 untrained male and female participants 10-14 years of age. Results: The results showed the influence of age in male participants on speed-strength performance, while in female participants, age did not significantly influence performance parameters. Moderate to high correlations between sprint and jump performance (r = 0.69-0.72), sprint and COD sprint performance (r = 0.58-0.72), and jump and COD sprint performance (r = 0.56-0.58) were found. Discussion: Based on the data from this study, it appears that the growth phase of age 10-14 does not necessarily lead to improvements in athletic performance. To ensure holistic motor development, female subjects in particular should be provided with specific training interventions with a focus on strength and power.
Keywords: change of direction; children; countermovement jump; squat jump; triangle test.
Copyright © 2023 Warneke, Wagner, Konrad, Kadlubowski, Sander, Wirth and Keiner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationships between Change of Direction, Sprint, Jump, and Squat Power Performance.Sports (Basel). 2020 Mar 19;8(3):38. doi: 10.3390/sports8030038. Sports (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32204331 Free PMC article.
-
Jump height ingenerated by countermovement and arm swing better correlates with proagility shuttle run tests but not with change of direction deficits in collegiate female athletes.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2024 Aug;64(8):749-757. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.24.15691-5. Epub 2024 Apr 10. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2024. PMID: 38602034
-
Accentuated Eccentric Loading in Countermovement Jumps Vs. Drop Jumps: Effects on Jump Performance and Strength in A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Sports Sci Med. 2025 Mar 1;24(1):20-30. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2025.20. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Sports Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 40046213 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of plyometric jump training on physical fitness attributes in basketball players: A meta-analysis.J Sport Health Sci. 2022 Nov;11(6):656-670. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Sport Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 33359798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness of resisted movement training on sprinting and jumping performance.J Strength Cond Res. 2012 Jan;26(1):299-306. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182185186. J Strength Cond Res. 2012. PMID: 22158137 Review.
Cited by
-
An 8-week exergame-based exercise training program improves cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength and endurance performances among primary school children in Taiwan.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jul 3;13:1566838. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1566838. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40677289 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Age and Playing Position on Field-Based Physical Fitness Measures in Adolescent Female Netball Players.Pediatr Rep. 2024 Jan 12;16(1):77-87. doi: 10.3390/pediatric16010008. Pediatr Rep. 2024. PMID: 38251317 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

