Network meta-analysis of the prognosis of curative treatment strategies for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy
- PMID: 36896302
- PMCID: PMC9988642
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i2.258
Network meta-analysis of the prognosis of curative treatment strategies for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy
Abstract
Background: Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (rHCC) is a common outcome after curative treatment. Retreatment for rHCC is recommended, but no guidelines exist.
Aim: To compare curative treatments such as repeated hepatectomy (RH), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and liver transplantation (LT) for patients with rHCC after primary hepatectomy by conducting a network meta-analysis (NMA).
Methods: From 2011 to 2021, 30 articles involving patients with rHCC after primary liver resection were retrieved for this NMA. The Q test was used to assess heterogeneity among studies, and Egger's test was used to assess publication bias. The efficacy of rHCC treatment was assessed using disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
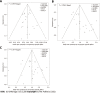
Results: From 30 articles, a total of 17, 11, 8, and 12 arms of RH, RFA, TACE, and LT subgroups were collected for analysis. Forest plot analysis revealed that the LT subgroup had a better cumulative DFS and 1-year OS than the RH subgroup, with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.96 (95%CI: 0.31-2.96). However, the RH subgroup had a better 3-year and 5-year OS compared to the LT, RFA, and TACE subgroups. Hierarchic step diagram of different subgroups measured by the Wald test yielded the same results as the forest plot analysis. LT had a better 1-year OS (OR: 1.04, 95%CI: 0.34-03.20), and LT was inferior to RH in 3-year OS (OR: 10.61, 95%CI: 0.21-1.73) and 5-year OS (OR: 0.95, 95%CI: 0.39-2.34). According to the predictive P score evaluation, the LT subgroup had a better DFS, and RH had the best OS. However, meta-regression analysis revealed that LT had a better DFS (P < 0.001) as well as 3-year OS (P = 0.881) and 5-year OS (P = 0.188). The differences in superiority between DFS and OS were due to the different testing methods used.
Conclusion: According to this NMA, RH and LT had better DFS and OS for rHCC than RFA and TACE. However, treatment strategies should be determined by the recurrent tumor characteristics, the patient's general health status, and the care program at each institution.
Keywords: Curative treatment; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Network meta-analysis; Outcome; Recurrence; Survival rate.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Optimal treatment strategy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma based on recurrence time and tumor size: A propensity score matching study.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug;47(7):102157. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2023.102157. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37321321
-
Efficacy of repeat hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a Systematic Review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 26;15:1559491. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1559491. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40206586 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation versus hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after initial surgery: a propensity score matching study.Eur Radiol. 2018 Aug;28(8):3522-3531. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5166-4. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29536241
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 27;20(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01544-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33246417 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-arterial chemoembolization + radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection in hepatocellular carcinoma - A meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020 May;46(5):763-771. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.01.004. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31937433 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing transarterial chemoembolization alone to combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation in primary hepatocellular carcinoma treatment.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):102038. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.102038. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40235864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Health Promotion Administration Ministry of Health and Welfare Taiwan Cancer Registry Annual Report, 2019, Taiwan. 2021: 2-5 [cited 21 Jun 2022]. Available from: https://wwwhpagovtw/Pages/Detailaspx?nodeid=269&pid=14913 .
-
- Zhang X, Li C, Wen T, Yan L, Li B, Yang J, Wang W, Xu M, Lu W, Jiang L. Appropriate treatment strategies for intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma initially within the Milan criteria: according to the recurrence pattern. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol . 2015;27:933–940. - PubMed
-
- Kaibori M, Kon M, Kitawaki T, Kawaura T, Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Ariizumi S, Beppu T, Ishizu H, Kubo S, Kamiyama T, Takamura H, Kobayashi T, Kim DS, Wang HJ, Kim JM, Han DH, Park SJ, Kang KJ, Hwang S, Roh Y, You YK, Joh JW, Yamamoto M. Comparison of anatomic and non-anatomic hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci . 2017;24:616–626. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

