Cell context-dependent CFI-1/ARID3 functions control neuronal terminal differentiation
- PMID: 36897776
- PMCID: PMC10124151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112220
Cell context-dependent CFI-1/ARID3 functions control neuronal terminal differentiation
Abstract
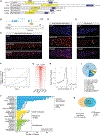
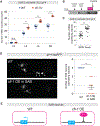
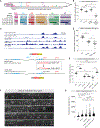
AT-rich interaction domain 3 (ARID3) transcription factors are expressed in the nervous system, but their mechanisms of action are largely unknown. Here, we provide, in vivo, a genome-wide binding map for CFI-1, the sole C. elegans ARID3 ortholog. We identify 6,396 protein-coding genes as putative direct targets of CFI-1, most of which encode neuronal terminal differentiation markers. In head sensory neurons, CFI-1 directly activates multiple terminal differentiation genes, thereby acting as a terminal selector. In motor neurons, however, CFI-1 acts as a direct repressor, continuously antagonizing three transcriptional activators. By focusing on the glr-4/GRIK4 glutamate receptor locus, we identify proximal CFI-1 binding sites and histone methyltransferase activity as necessary for glr-4 repression. Rescue assays reveal functional redundancy between core and extended DNA-binding ARID domains and a strict requirement for REKLES, the ARID3 oligomerization domain. Altogether, this study uncovers cell-context-dependent mechanisms through which a single ARID3 protein controls the terminal differentiation of distinct neuron types.
Keywords: ARID proteins; ARID3; C. elegans; CFI-1; CP: Neuroscience; CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing; ChIP-seq; neuronal differentiation; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wilsker D, Patsialou A, Dallas PB, and Moran E (2002). ARID proteins: a diverse family of DNA binding proteins implicated in the control of cell growth, differentiation, and development. Cell Growth Differ. 13, 95–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

