In situ amplification of spin echoes within a kinetic inductance parametric amplifier
- PMID: 36897947
- PMCID: PMC10005168
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg1593
In situ amplification of spin echoes within a kinetic inductance parametric amplifier
Abstract
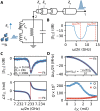
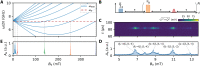
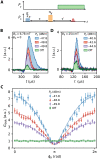
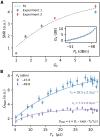
The use of superconducting microresonators together with quantum-limited Josephson parametric amplifiers has enhanced the sensitivity of pulsed electron spin resonance (ESR) measurements by more than four orders of magnitude. So far, the microwave resonators and amplifiers have been designed as separate components due to the incompatibility of Josephson junction-based devices with magnetic fields. This has produced complex spectrometers and raised technical barriers toward adoption of the technique. Here, we circumvent this issue by coupling an ensemble of spins directly to a weakly nonlinear and magnetic field-resilient superconducting microwave resonator. We perform pulsed ESR measurements with a 1-pL mode volume containing 6 × 107 spins and amplify the resulting signals within the device. When considering only those spins that contribute to the detected signals, we find a sensitivity of [Formula: see text] for a Hahn echo sequence at a temperature of 400 mK. In situ amplification is demonstrated at fields up to 254 mT, highlighting the technique's potential for application under conventional ESR operating conditions.
Figures
References
-
- A. Schweiger, G. Jeschke, Principles of pulse electron paramagnetic resonance (Oxford Univ. Press, 2001).
-
- S. Haroche, J.-M. Raimond, Exploring the Quantum: Atoms, Cavities and Photons (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
-
- J. J. L. Morton, P. Bertet, Storing quantum information in spins and high-sensitivity esr. J. Magn. Reson. 287, 128–139 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Y. Artzi, Y. Yishay, M. Fanciulli, M. Jbara, A. Blank, Superconducting micro-resonators for electron spin resonance-the good, the bad, and the future. J. Magn. Reson. 334, 107102 (2022). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

