From PROTAC to inhibitor: Structure-guided discovery of potent and orally bioavailable BET inhibitors
- PMID: 36898329
- PMCID: PMC10165889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115246
From PROTAC to inhibitor: Structure-guided discovery of potent and orally bioavailable BET inhibitors
Abstract
An X-ray structure of a CLICK chemistry-based BET PROTAC bound to BRD2(BD2) inspired synthesis of JQ1 derived heterocyclic amides. This effort led to the discovery of potent BET inhibitors displaying overall improved profiles when compared to JQ1 and birabresib. A thiadiazole derived 1q (SJ1461) displayed excellent BRD4 and BRD2 affinity and high potency in the panel of acute leukaemia and medulloblastoma cell lines. A structure of 1q co-crystalised with BRD4-BD1 revealed polar interactions with the AZ/BC loops, in particular with Asn140 and Tyr139, rationalising the observed affinity improvements. In addition, exploration of pharmacokinetic properties of this class of compounds suggest that the heterocyclic amide moiety improves drug-like features. Our study led to the discovery of potent and orally bioavailable BET inhibitor 1q (SJ1461) as a promising candidate for further development.
Keywords: Amides; BET inhibitors; JQ1.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: ZR, MF, WCKP reports financial support was provided by ALSAC. VS reports financial support was provided by The Science Fund of The Republic of Serbia.
Figures
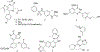


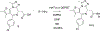
Similar articles
-
Discovery and characterization of bromodomain 2-specific inhibitors of BRDT.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 2;118(9):e2021102118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021102118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33637650 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the First BRD4 Second Bromodomain (BD2)-Selective Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 12;67(23):21577-21616. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02516. Epub 2024 Nov 27. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39602227
-
Structure-Based Discovery of CF53 as a Potent and Orally Bioavailable Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Bromodomain Inhibitor.J Med Chem. 2018 Jul 26;61(14):6110-6120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00483. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30015487 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule PROTAC degraders of the Bromodomain and Extra Terminal (BET) proteins - A review.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2019 Apr;31:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 May 1. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2019. PMID: 31200858 Review.
-
Recent Developments in Targeting Bromodomain and Extra Terminal Domain Proteins for Cancer Therapeutics.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(25):4391-4409. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220211091806. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35152859 Review.
Cited by
-
Medulloblastoma in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA): Bridging Pediatric Paradigms and Adult Oncology Practice.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 24;14(13):4472. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134472. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40648846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hnilica LS, Structure and Biological Functions of Histones, 1st edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017.
-
- Shen C, ed., Histones: Class, Structure and Function, 1st edition, Nova Science Pub Inc, New York, 2012.
-
- Lee CY, Grant PA, Chapter 1–1 - Role of Histone Acetylation and Acetyltransferases in Gene Regulation, in: McCullough SD, Dolinoy DC (Eds.), Toxicoepigenetics, Academic Press, 2019: pp. 3–30.10.1016/B978-0-12-812433-8.00001-0. - DOI
-
- Struhl K, Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms, Genes Dev. 12 (1998) 599–606. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

