Quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate booster vaccination in adolescents and adults: phase III randomized study
- PMID: 36899125
- PMCID: PMC10000353
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-023-02478-5
Quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate booster vaccination in adolescents and adults: phase III randomized study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Quadrivalent meningococcal tetanus toxoid-conjugate booster vaccination in adolescents and adults: phase III randomized study.Pediatr Res. 2024 Mar;95(4):1159. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02835-4. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37853068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The immunogenicity and safety of a booster dose of tetanus toxoid-conjugate quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine (MenACYW-TT), alone or co-administered with MenB vaccine, were assessed in healthy 13-25-year olds who received MenACYW-TT or a CRM-conjugate vaccine (MCV4-CRM) 3-6 years earlier.
Methods: This phase IIIb open-label trial (NCT04084769) evaluated MenACYW-TT-primed participants, randomized to receive MenACYW-TT alone or with a MenB vaccine, and MCV4-CRM-primed participants who received MenACYW-TT alone. Functional antibodies against serogroups A, C, W and Y were measured using human complement serum bactericidal antibody assay (hSBA). The primary endpoint was vaccine seroresponse (post-vaccination titers ≥1:16 if pre-vaccination titers <1:8; or a ≥4-fold increase if pre-vaccination titers ≥1:8) 30 days post booster. Safety was evaluated throughout the study.
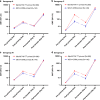
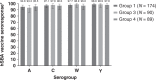
Results: The persistence of the immune response following primary vaccination with MenACYW-TT was demonstrated. Seroresponse after MenACYW-TT booster was high regardless of priming vaccine (serogroup A: 94.8% vs 93.2%; C: 97.1% vs 98.9%; W: 97.7% vs 98.9%; and Y; 98.9% vs 100% for MenACWY-TT-primed and MCV4-CRM-primed groups, respectively). Co-administration with MenB vaccines did not affect MenACWY-TT immunogenicity. No vaccine-related serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: MenACYW-TT booster induced robust immunogenicity against all serogroups, regardless of the primary vaccine received, and had an acceptable safety profile.
Impact: A booster dose of MenACYW-TT induces robust immune responses in children and adolescents primed with MenACYW-TT or another MCV4 (MCV4-DT or MCV4-CRM), respectively. Here, we demonstrate that MenACYW-TT booster 3-6 years after primary vaccination induced robust immunogenicity against all serogroups, regardless of the priming vaccine (MenACWY-TT or MCV4-CRM), and was well tolerated. Persistence of the immune response following previous primary vaccination with MenACYW-TT was demonstrated. MenACYW-TT booster with MenB vaccine co-administration did not affect MenACWY-TT immunogenicity and was well tolerated. These findings will facilitate the provision of broader protection against IMD particularly in higher-risk groups such as adolescents.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.Z., J.S., J.Pa., A.H., D.V.B., K.V., E.J. and M.S.D. are employees of Sanofi and may hold stocks/shares. C.D., K.J. and J.Pe. received funding from Sanofi to support work for the trial. B.B., R.H., M.S., C.Se., C.Sp. and M.A. have no conflicts of interest to declare. G.Á. was an employee of Sanofi at the time this study was conducted.
Figures


References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Factsheet about meningococcal disease. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/meningococcal-disease/factsheet, (accessed October 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

