Type 2 diabetes mellitus and In-hospital Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCEs) and postoperative complications among patients undergoing on-pump isolated coronary artery bypass surgery in Northeastern Iran
- PMID: 36899306
- PMCID: PMC10007752
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03163-5
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and In-hospital Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCEs) and postoperative complications among patients undergoing on-pump isolated coronary artery bypass surgery in Northeastern Iran
Abstract
Background: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a rapidly growing disorder worldwide, especially in the Middle East. A higher incidence of coronary artery diseases requiring coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery has been reported in patients with diabetes. We assessed the association between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and in-hospital major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs) and postoperative complications among patients who underwent on-pump isolated CABG.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we used the data registered for CABG patients from two heart centers in the Golestan province (North of Iran) between 2007 and 2016. The study population included 1956 patients divided into two groups: 1062 non-diabetic patients and 894 patients with diabetes (fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dl or using antidiabetic medications). The study outcome was in-hospital MACCEs, a composite outcome of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke and cardiovascular death, and postoperative complications, including postoperative arrhythmia, acute atrial fibrillation (AF), major bleeding (defined as reoperation due to bleeding), and acute kidney injury (AKI).
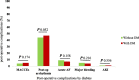
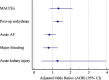
Results: During the 10-year study period, 1956 adult patients with a mean (SD) age of 59.0 (9.60) years were included. After adjustment for age, gender, ethnicity, obesity, opium consumption, and smoking, diabetes was a predictor of postoperative arrhythmia (AOR 1.30, 95% CI 1.08-1.57; P = 0.006). While it was not a predictor of in-hospital MACCEs (AOR 1.35, 95% CI 0.86, 2.11; P = 0.188), AF (AOR 0.85, 95% CI 0.60-1.19; P = 0.340), major bleeding (AOR 0.80, 95% CI 0.50, 1.30; P = 0.636) or AKI (AOR 1.29, 95% CI 0.42, 3.96; P 0.656) after CABG surgery.
Conclusion: Findings indicated that diabetes increased the risk of postoperative arrhythmia by 30%. However, we found similar in-hospital MACCEs, acute AF, major bleeding, and AKI following CABG surgery in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
Keywords: Complications; Coronary artery bypass; Diabetes Mellitus, Type2; Major adverse cardiovascular events; Retrospective studies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethnic Disparities in Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCEs) and Postoperative Outcomes Following Coronary Artery Bypass in Northeastern Iran (2007-2016).Arch Iran Med. 2023 Oct 1;26(10):554-560. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.81. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38310411 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of remnant cholesterol on short-term and long-term prognosis in patients with prediabetes or diabetes undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: a large-scale cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 8;24(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02537-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39780174 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing postoperative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting, single center experience.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017 May 23;12(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13019-017-0609-1. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28535775 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of diabetic patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery compared with nondiabetics: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011 Apr;25(2):288-98. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2010.09.021. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011. PMID: 21147538
-
Short-term outcomes of on- vs off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with left ventricular dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 May 11;15(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13019-020-01115-0. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32393284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of glucose coefficient of variation for in-hospital mortality in acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing PCI: Insights from the MIMIC-IV database.Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024 Oct 26;23:200347. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200347. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024. PMID: 39524973 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnic Disparities in Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCEs) and Postoperative Outcomes Following Coronary Artery Bypass in Northeastern Iran (2007-2016).Arch Iran Med. 2023 Oct 1;26(10):554-560. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.81. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38310411 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting postoperative atrial fibrillation in cardiac surgery.J Med Life. 2025 May;18(5):494-508. doi: 10.25122/jml-2025-0085. J Med Life. 2025. PMID: 40599146 Free PMC article.
-
The Pandemic of Coronary Heart Disease in the Middle East and North Africa: What Clinicians Need to Know.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023 Sep;25(9):543-557. doi: 10.1007/s11883-023-01126-x. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023. PMID: 37615785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global report on diabetes. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

