Do NAAT-Based Methods Increase the Diagnostic Sensitivity of Streptococcus agalactiae Carriage Detection in Pregnant Women?
- PMID: 36900007
- PMCID: PMC10001255
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13050863
Do NAAT-Based Methods Increase the Diagnostic Sensitivity of Streptococcus agalactiae Carriage Detection in Pregnant Women?
Abstract
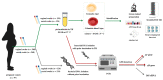
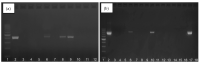
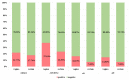
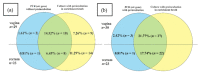
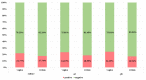
The aim of the study was to evaluate particular polymerase chain reaction primers targeting selected representative genes and the influence of a preincubation step in a selective broth on the sensitivity of group B Streptococcus (GBS) detection by nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAAT). Research samples were vaginal and rectal swabs collected in duplicate from 97 pregnant women. They were used for enrichment broth culture-based diagnostics, bacterial DNA isolation, and amplification, using primers based on species-specific 16S rRNA, atr and cfb genes. To assess the sensitivity of GBS detection, additional isolation of samples preincubated in Todd-Hewitt broth with colistin and nalidixic acid was performed and then subjected to amplification again. The introduction of the preincubation step increased the sensitivity of GBS detection by about 33-63%. Moreover, NAAT made it possible to identify GBS DNA in an additional six samples that were negative in culture. The highest number of true positive results compared to the culture was obtained with the atr gene primers, as compared to cfb and 16S rRNA primers. Isolation of bacterial DNA after preincubation in enrichment broth significantly increases the sensitivity of NAAT-based methods applied for the detection of GBS from vaginal and rectal swabs. In the case of the cfb gene, the use of an additional gene to ensure the appropriate results should be considered.
Keywords: GBS; PCR; Streptococcus agalactiae; pregnant women; primers; real-time PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- American Society for Microbiology—Guidelines for the Detection and Identification of Group B Streptococcus. [(accessed on 19 December 2022)]. Available online: https://asm.org/Guideline/Guidelines-for-the-Detection-and-Identificatio....
-
- Brzychczy-Włoch M., Pabian W., Majewska E., Żuk M., Kiełbik J., Gosiewski T., Bulanda M. Dynamics of colonization with group B streptococci in relation to normal flora in women during subsequent trimesters of pregnancy. New Microbiol. 2014;37:307–319. - PubMed
-
- Sroka-Oleksiak A., Gosiewski T., Pabian W., Gurgul A., Kapusta P., Ludwig-Słomczyńska A.H., Wołkow P.P., Brzychczy-Włoch M. Next-Generation Sequencing as a Tool to Detect Vaginal Microbiota Disturbances during Pregnancy. Microorganisms. 2020;8:1813. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

