Insomnia-A Systematic Review and Comparison of Medical Resident's Average Off-Call Sleep Times
- PMID: 36901190
- PMCID: PMC10002061
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20054180
Insomnia-A Systematic Review and Comparison of Medical Resident's Average Off-Call Sleep Times
Abstract
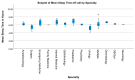
Sleep deprivation is known to have serious consequences, including a decrease in performance, attention and neurocognitive function. It seems common knowledge that medical residents are routinely sleep deprived, yet there is little objective research recording their average sleep times. To discern whether residents may be suffering from the abovementioned side effects, this review aimed to analyze their average sleep times. Thirty papers recording the average sleep time of medical residents were found via a literature search using the key words "resident" and "sleep". An analysis of the mean sleep times cited therein revealed a range of sleep from 4.2 to 8.6 h per night, the median being 6.2 h. A sub-analysis of papers from the USA showed barely any significant differences in sleep time between the specialties, but the mean sleep times were below 7 h. The only significant difference (p = 0.039) was between the mean sleep times of pediatric and urology residents, with the former achieving less sleep. The comparison of methods for data collection showed no significant difference in the sleep times collected. The results of this analysis imply that residents are regularly sleep deprived and may therefore suffer from the abovementioned consequences.
Keywords: residency; sleep; sleep deprivation; sleep times; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Watson N.F., Badr M.S., Belenky G., Bliwise D.L., Buxton O., Buysse D., Dinges D.F., Gangwisch J., Grandner M.A., Kushida C., et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for a Healthy Adult: A Joint Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep. 2015;38:843–844. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4716. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huizinga C.R.H., de Kam M., Stockmann H., van Gerven J., Cohen A., van der Bogt K.E.A. Evaluating Fitness to Perform in Surgical Residents after Night Shifts and Alcohol Intoxication: The development of a “Fit-to-Perform” test. J. Surg. Educ. 2018;75:968–977. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2018.01.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

