Auditing the Audits: A Systematic Review on Different Procedures in Telemedicine
- PMID: 36901491
- PMCID: PMC10001883
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20054484
Auditing the Audits: A Systematic Review on Different Procedures in Telemedicine
Abstract
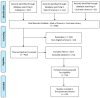
Telemedicine is a process of delivering health care using information and communication technologies. Audit and feedback (A&F) constitute a systematic intervention that is aimed at collecting data, which are subsequently compared with reference standards and then returned to health care operators through feedback meetings. The aim of this review is to analyse different audit procedures on and by mean of telemedicine services and to identify a practice that is more effective than the others. Systematic searches were performed in three databases evaluating studies focusing on clinical audits performed on and by means of telemedicine systems. Twenty-five studies were included in the review. Most of them focused on telecounselling services with an audit and a maximum duration of one year. Recipients of the audit were telemedicine systems and service users (general practitioners, referring doctors, and patients). Data resulting from the audit were inherent to the telemedicine service. The overall data collected concerned the number of teleconsultations, service activity, reasons for referral, response times, follow-up, reasons why treatment was not completed, technical issues, and other information specific to each telemedicine service. Only two of the considered studies dealt with organizational aspects, and of these, only one analysed communicative aspects. The complexity and heterogeneity of the treatments and services provided meant that no index of uniformity could be identified. Certainly, some audits were performed in an overlapping manner in the different studies, and these show that although attention is often paid to workers' opinions, needs, and issues, little interest was shown in communicative/organizational and team dynamics. Given the importance and influence that communication has in teamwork and care settings, an audit protocol that takes into account intra- and extra-team communication processes could be essential to improving the well-being of operators and the quality of the service provided.
Keywords: EASY-NET; audit; feedback; telecare; telehealth; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Nesbitt T.S. The Evolution of Telehealth: Where Have We Been and Where Are We Going. National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2012.
-
- Blackburn H. Translation of The Telecardiogram, article by W. Einthoven. Am. Heart J. 1957;53:602–615.
-
- Lai F. Robotic telepresence for collaborative clinical outreach. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2008;132:233–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical