Social Distancing and Shopping Behaviour: The Role of Anxiety, Attention, and Awareness on Safety Preferences while Queuing during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 36901599
- PMCID: PMC10001668
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20054589
Social Distancing and Shopping Behaviour: The Role of Anxiety, Attention, and Awareness on Safety Preferences while Queuing during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
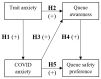
The COVID-19 pandemic increased global anxiety, and many people shopped less frequently. This study quantifies customer preferences in where to shop while following social distancing regulations, specifically focusing on customers' anxiety. Collecting data online from 450 UK participants, we measured trait anxiety, COVID-19 anxiety, queue awareness, and queue safety preferences. Confirmatory factor analyses were used to develop novel queue awareness and queue safety preference variables from new items. Path analyses tested the hypothesised relationships between them. Queue awareness and COVID-19 anxiety were positive predictors of queue safety preference, with queue awareness partially mediating the effect of COVID-19 anxiety. These results suggest that customers' preferences for shopping at one business and not another may depend on safe queueing and waiting conditions, especially in those more anxious about COVID-19 transmission. Interventions that target highly aware customers are suggested. Limitations are acknowledged and areas for future development are outlined.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 anxiety; anxiety; coronavirus; pandemic; queue; queue environment; queueing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sood S. Psychological effects of the Coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic. [(accessed on 25 January 2023)];Res. Humanit. Med. Educ. 2020 7:23–26. Available online: https://www.rhime.in/ojs/index.php/rhime/article/view/264.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

