Topical Diacerein Decreases Skin and Splenic CD11c+ Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis
- PMID: 36901755
- PMCID: PMC10001455
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054324
Topical Diacerein Decreases Skin and Splenic CD11c+ Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis
Abstract
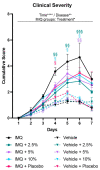
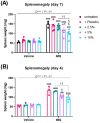
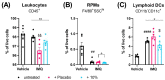
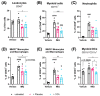
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by increased neo-vascularization, keratinocyte hyperproliferation, a pro-inflammatory cytokine milieu and immune cell infiltration. Diacerein is an anti-inflammatory drug, modulating immune cell functions, including expression and production of cytokines, in different inflammatory conditions. Therefore, we hypothesized that topical diacerein has beneficial effects on the course of psoriasis. The current study aimed to evaluate the effect of topical diacerein on imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis in C57BL/6 mice. Topical diacerein was observed to be safe without any adverse side effects in healthy or psoriatic animals. Our results demonstrated that diacerein significantly alleviated the psoriasiform-like skin inflammation over a 7-day period. Furthermore, diacerein significantly diminished the psoriasis-associated splenomegaly, indicating a systemic effect of the drug. Remarkably, we observed significantly reduced infiltration of CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) into the skin and spleen of psoriatic mice with diacerein treatment. As CD11c+ DCs play a pivotal role in psoriasis pathology, we consider diacerein to be a promising novel therapeutic candidate for psoriasis.
Keywords: dendritic cell; diacerein; imiquimod; psoriasis; rhein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Grozdev I., Kast D., Cao L., Carlson D., Pujari P., Schmotzer B., Babineau D., Kern E., McCormick T., Cooper K.D., et al. Physical and mental impact of psoriasis severity as measured by the compact Short Form-12 Health Survey (SF-12) quality of life tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012;132:1111–1116. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

