Genome-Wide Investigation of the NAC Transcription Factor Family in Apocynum venetum Revealed Their Synergistic Roles in Abiotic Stress Response and Trehalose Metabolism
- PMID: 36902009
- PMCID: PMC10003206
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054578
Genome-Wide Investigation of the NAC Transcription Factor Family in Apocynum venetum Revealed Their Synergistic Roles in Abiotic Stress Response and Trehalose Metabolism
Abstract
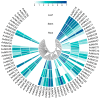
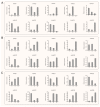
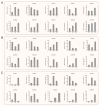
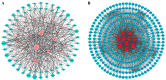
NAC (NAM, ATAF1/2, and CUC2) transcription factors (TFs) are one of the most prominent plant-specific TF families and play essential roles in plant growth, development and adaptation to abiotic stress. Although the NAC gene family has been extensively characterized in many species, systematic analysis is still relatively lacking in Apocynum venetum (A. venetum). In this study, 74 AvNAC proteins were identified from the A. venetum genome and were classified into 16 subgroups. This classification was consistently supported by their gene structures, conserved motifs and subcellular localizations. Nucleotide substitution analysis (Ka/Ks) showed the AvNACs to be under the influence of strong purifying selection, and segmental duplication events were found to play the dominant roles in the AvNAC TF family expansion. Cis-elements analysis demonstrated that the light-, stress-, and phytohormone-responsive elements being dominant in the AvNAC promoters, and potential TFs including Dof, BBR-BPC, ERF and MIKC_MADS were visualized in the TF regulatory network. Among these AvNACs, AvNAC58 and AvNAC69 exhibited significant differential expression in response to drought and salt stresses. The protein interaction prediction further confirmed their potential roles in the trehalose metabolism pathway with respect to drought and salt resistance. This study provides a reference for further understanding the functional characteristics of NAC genes in the stress-response mechanism and development of A. venetum.
Keywords: NAC transcription factor; drought stress; salt stress; trehalose metabolism pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PP2C gene family in Apocynum venetum and Apocynum hendersonii.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05328-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38982365 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide characterization of R2R3 MYB transcription factor from Apocynum venetum revealed potential stress tolerance and flavonoid biosynthesis genes.Genomics. 2022 Mar;114(2):110275. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110275. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35108591
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Role of NAC Family in Flower Development and Abiotic Stress Responses in Cleistogenes songorica.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 12;11(8):927. doi: 10.3390/genes11080927. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32806602 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of the non-specific lipid transfer protein gene family in Nicotiana tabacum reveal its potential roles in stress responses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Feb 1;172:33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35016104 Review.
-
Multiple roles of NAC transcription factors in plant development and stress responses.J Integr Plant Biol. 2025 Mar;67(3):510-538. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13854. Epub 2025 Feb 14. J Integr Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39950532 Review.
Cited by
-
Abiotic Stress Tolerance Boosted by Genetic Diversity in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 14;25(10):5367. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105367. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791404 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Steroidal Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Bulbs of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. By Shading and Potassium Application: Integrating Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Analyses.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 29;14(6):633. doi: 10.3390/biology14060633. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563884 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PP2C gene family in Apocynum venetum and Apocynum hendersonii.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05328-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38982365 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiles Reveals ScDREB10 from Syntrichia caninervis Regulated Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis and Starch/Sucrose Metabolism to Enhance Plant Stress Tolerance.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;13(2):205. doi: 10.3390/plants13020205. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256758 Free PMC article.
-
Genome identification of NAC gene family and its gene expression patterns in responding to salt and drought stresses in Rhododendron delavayi.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 17;25(1):924. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06965-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40676511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen M.K., Rung J.H., Gregersen P.L., Gjetting T., Fuglsang A.T., Hansen M., Joehnk N., Lyngkjaer M.F., Collinge D.B. The HvNAC6 transcription factor: A positive regulator of penetration resistance in barley and Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007;65:137–150. doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9204-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

