Polydeoxyribonucleotide in the Treatment of Tendon Disorders, from Basic Science to Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36902012
- PMCID: PMC10002571
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054582
Polydeoxyribonucleotide in the Treatment of Tendon Disorders, from Basic Science to Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review
Abstract
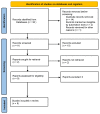
Polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) is a proprietary and registered drug with several beneficial effects, including tissue repairing, anti-ischemic action, and anti-inflammatory properties. The present study aims to summarize the current evidence about PRDN's clinical effectiveness in the management of tendon disorders. From January 2015 to November 2022, OVID-MEDLINE®, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, SCOPUS, Web of Science, Google Scholar and PubMed were searched to identify relevant studies. The methodological quality of the studies was evaluated, and relevant data were extracted. Nine studies (two in vivo studies and seven clinical studies) were finally included in this systematic review. Overall, 169 patients (male: 103) were included in the present study. The effectiveness and safeness of PDRN has been investigated in the management of the following diseases: plantar fasciitis; epicondylitis; Achilles tendinopathy; pes anserine bursitis; chronic rotator cuff disease. No adverse effects have been recorded in the included studies and all the patients showed an improvement in clinical symptoms during the follow-up. PDRN are a valid emerging therapeutic drug in the treatment of tendinopathies. Further multicentric randomized clinical studies are needed to better define the therapeutic role of PDRN, especially in combined clinical protocols.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; ESWT; PDRN; fasciitis; lateral epicondylitis; musculoskeletal pain; rotator cuff disease; tendinitis; tendinopathies; tendon diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrotherapy modalities for rotator cuff disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 10;2016(6):CD012225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012225. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27283591 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: results and indications.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018 Jul;26(7):1984-1999. doi: 10.1007/s00167-016-4261-4. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018. PMID: 27665095
-
Physiotherapy interventions for shoulder pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;2003(2):CD004258. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004258. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12804509 Free PMC article.
-
Manual therapy and exercise for rotator cuff disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 10;2016(6):CD012224. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012224. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27283590 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies Supporting the Role of Polydeoxyribonucleotide in the Treatment of Tendon Disorders.Med Sci Monit. 2025 Apr 7;31:e945743. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945743. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 40189862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Melatonin and Polydeoxyribonucleotide: Possible Benefits of Co-Treatment Effects and Potential Synergistic Applicability.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 13;26(12):5703. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125703. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Adenosine Signalling in Knee Chondropathy: The Combined Action of Polydeoxyribonucleotide and Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields: A Current Concept Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 13;24(12):10090. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210090. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Polydeoxyribonucleic Acid (PDRN) in periodontal regeneration: A systematic review of clinical outcomes.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025 May-Jun;15(3):624-630. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.03.021. Epub 2025 Apr 9. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025. PMID: 40256760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical