Pyodermitis during Nivolumab Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 36902013
- PMCID: PMC10003408
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054580
Pyodermitis during Nivolumab Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
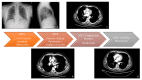
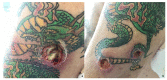
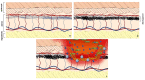
Immunotherapy in oncology is replacing traditional therapies due to it specific action and limited side effects. Despite the high efficacy of immunotherapy, side effects such as bacterial infection have been reported. Bacterial skin and soft tissue infections represent one of the most important differential diagnoses in patients presenting with reddened and swollen skin and soft tissue. Among these infections, cellulitis (phlegmon) and abscesses are the most frequent. In most cases, these infections occur locally with possible contiguous spread, or as a multifocal manifestation, especially in immunocompromised patients. Herein, we report a case of pyodermitis in an immunocompromised district in a patient treated with nivolumab for non-small cell lung cancer. A 64-year-old, smoker male patient showed cutaneous lesions at a different evolution level in the left arm, all in a tattooed area, with one phlegmon and two ulcerated lesions. Microbiological cultures and gram staining revealed an infection caused by a methicillin-susceptible but erythromycin-resistant (ER-R), clindamycin-resistant (CL-R), and gentamicin-resistant (GE-R) Staphylococcus aureus strain. Despite immunotherapy becoming a milestone in oncologic treatment, more than the spectrum of immune-mediated toxicities of these agents needs to be investigated. This report highlights the importance of considering lifestyle and cutaneous background before starting immunotherapy for cancer treatment, with an emphasis on pharmacogenomics and the possibility of modified skin microbiota predisposing to cutaneous infections in patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; cutaneous infection; immunotherapy; nivolumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Topalian S.L., Hodi F.S., Brahmer J.R., Gettinger S.N., Smith D.C., McDermott D.F., Powderly J.D., Carvajal R.D., Sosman J.A., Atkins M.B., et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:2443–2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brahmer J.R., Govindan R., Anders R.A., Antonia S.J., Sagorsky S., Davies M.J., Dubinett S.M., Ferris A., Gandhi L., Garon E.B., et al. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) J. Immunother. Cancer. 2018;6:75. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0382-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

