Low Dose of BPA Induces Liver Injury through Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Long-Evans Lactating Rats and Its Perinatal Effect on Female PND6 Offspring
- PMID: 36902016
- PMCID: PMC10002922
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054585
Low Dose of BPA Induces Liver Injury through Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Long-Evans Lactating Rats and Its Perinatal Effect on Female PND6 Offspring
Abstract
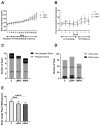
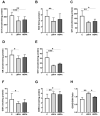
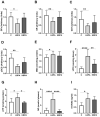
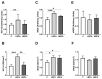
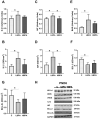
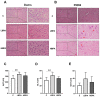
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a phenolic compound used in plastics elaboration for food protection or packaging. BPA-monomers can be released into the food chain, resulting in continuous and ubiquitous low-dose human exposure. This exposure during prenatal development is especially critical and could lead to alterations in ontogeny of tissues increasing the risk of developing diseases in adulthood. The aim was to evaluate whether BPA administration (0.036 mg/kg b.w./day and 3.42 mg/kg b.w./day) to pregnant rats could induce liver injury by generating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis, and whether these effects may be observed in female postnatal day-6 (PND6) offspring. Antioxidant enzymes (CAT, SOD, GR, GPx and GST), glutathione system (GSH/GSSG) and lipid-DNA damage markers (MDA, LPO, NO, 8-OHdG) were measured using colorimetric methods. Inducers of oxidative stress (HO-1d, iNOS, eNOS), inflammation (IL-1β) and apoptosis (AIF, BAX, Bcl-2 and BCL-XL) were measured by qRT-PCR and Western blotting in liver of lactating dams and offspring. Hepatic serum markers and histology were performed. Low dose of BPA caused liver injury in lactating dams and had a perinatal effect in female PND6 offspring by increasing oxidative stress levels, triggering an inflammatory response and apoptosis pathways in the organ responsible for detoxification of this endocrine disruptor.
Keywords: apoptosis; bisphenol A; inflammation; liver injury; oxidative stress; perinatal offspring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
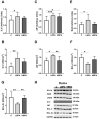
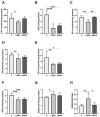
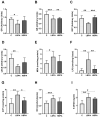
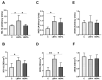

Similar articles
-
DINCH Exposure Triggers Inflammatory, Oxidative, and Apoptotic Pathways in the Liver of Long-Evans Lactating Rats and Their Offspring.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 3;25(23):13017. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313017. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684727 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress increases in liver of lactating rats after BPF-low-dose exposure: perinatal effects in the offspring.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 11;13(1):11229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38434-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37433837 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Liver of Long Evans Lactating Rats and Its Perinatal Effects in the Offspring after Bisphenol F Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 15;24(18):14129. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814129. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762434 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in BPA-induced Oxidative Stress and Related Effects and Mechanisms in Liver, 1991-2017.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(6):432-443. doi: 10.2174/1389557518666180912105345. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30207228 Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and BPA Toxicity: An Antioxidant Approach for Male and Female Reproductive Dysfunction.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 10;9(5):405. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050405. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397641 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 13;16(12):1859. doi: 10.3390/nu16121859. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931214 Free PMC article.
-
Bombesin-like receptor 3 expression induced by bisphenol A is likely associated with reduced cell proliferation by inhibiting DNA synthesis and inducing inflammation in liver cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 1;51(1):271. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09080-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38302795
-
DINCH Exposure Triggers Inflammatory, Oxidative, and Apoptotic Pathways in the Liver of Long-Evans Lactating Rats and Their Offspring.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 3;25(23):13017. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313017. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684727 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of exposure to bisphenol-A or parabens with markers of liver injury/function among US adults in NHANES 2011-2016.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2025 Jul;35(4):611-618. doi: 10.1038/s41370-024-00704-8. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 39020160
-
Liver and Pancreatic Toxicity of Endocrine-Disruptive Chemicals: Focus on Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 6;25(13):7420. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137420. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000526 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acaroz U., Ince S., Arslan-Acaroz D., Gurler Z., Demirel H.H., Kucukkurt I., Eryavuz A., Kara R., Varol N., Zhu K. Bisphenol-A Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Gene Expression, and Metabolic and Histopathological Changes in Male Wistar Albino Rats: Protective Role of Boron. Toxicol. Res. 2019;8:262–269. doi: 10.1039/C8TX00312B. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peerapanyasut W., Kobroob A., Palee S., Chattipakorn N., Wongmekiat O. Activation of Sirtuin 3 and Maintenance of Mitochondrial Integrity by N-Acetylcysteine Protects against Bisphenol A-Induced Kidney and Liver Toxicity in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:267. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

