Recent Advances in Green Metallic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery in Photodynamic Therapy: A Therapeutic Approach
- PMID: 36902238
- PMCID: PMC10003542
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054808
Recent Advances in Green Metallic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery in Photodynamic Therapy: A Therapeutic Approach
Abstract
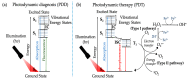
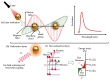
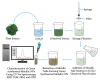
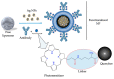
Globally, cancer is one of the leading causes of death among men and women, it is characterized by the unregulated proliferation of tumor cells. Some of the common risk factors associated with cancer development include the consistent exposure of body cells to carcinogenic agents such as alcohol, tobacco, toxins, gamma rays and alpha particles. Besides the above-mentioned risk factors, conventional therapies such as radiotherapy, and chemotherapy have also been linked to the development of cancer. Over the past decade, tremendous efforts have been invested in the synthesis of eco-friendly green metallic nanoparticles (NPs), and their medical application. Comparatively, metallic NPs have greater advantages over conventional therapies. Additionally, metallic NPs can be functionalized with different targeting moieties e.g., liposomes, antibodies, folic acid, transferrin, and carbohydrates. Herein, we review and discuss the synthesis, and therapeutic potential of green synthesized metallic NPs for enhanced cancer photodynamic therapy (PDT). Finally, the advantages of green hybridized activatable NPs over conventional photosensitizers (PSs) and the future perspectives of nanotechnology in cancer research are discussed in the review. Furthermore, we anticipate that the insights offered in this review will inspire the design and development of green nano-formulations for enhanced image-guided PDT in cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer; nanoparticles; photodynamic therapy; photosensitizer; theranostic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review on singlet oxygen generation in nanomaterials and conjugated polymers for photodynamic therapy in the treatment of cancer.Nanoscale. 2024 Feb 15;16(7):3243-3268. doi: 10.1039/d3nr05801h. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38265094 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Photosensitizers as Multifunctional Theranostic Agents for Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Aug 26;11(18):9054-9088. doi: 10.7150/thno.62479. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34522227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in chlorin-based photodynamic therapy with nanoparticle delivery system for cancer treatment.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Oct;18(10):1473-1500. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2021.1950685. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34253129 Review.
-
Photodynamic cancer therapy using liposomes as an advanced vesicular photosensitizer delivery system.J Control Release. 2021 Nov 10;339:75-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.09.024. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 34562540 Review.
-
Natural-product-based, carrier-free, noncovalent nanoparticles for tumor chemo-photodynamic combination therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2024 May;203:107150. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107150. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38521285 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Photodynamic Therapy: Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Tools to Improve Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 12;16(7):932. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070932. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Nanomaterials for Smart Textiles Dedicated to Environmental and Biomedical Applications.Materials (Basel). 2023 May 30;16(11):4075. doi: 10.3390/ma16114075. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37297209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal nanoparticles as a potential technique for the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 19;23(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03115-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37981671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials: A Review from the Standpoint of Pharmacy and Medicine.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 16;17(5):655. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050655. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting triple negative breast cancer stem cells using nanocarriers.Discov Nano. 2024 Mar 7;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s11671-024-03985-y. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 38453756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lismont M., Dreesen L., Wuttke S. Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy: Current Status and Perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017;27:1606314. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201606314. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

