Oral Submucous Fibrosis: Etiological Mechanism, Malignant Transformation, Therapeutic Approaches and Targets
- PMID: 36902423
- PMCID: PMC10003551
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24054992
Oral Submucous Fibrosis: Etiological Mechanism, Malignant Transformation, Therapeutic Approaches and Targets
Abstract
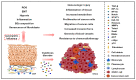
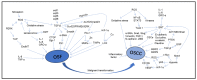
Oral submucosal fibrosis (OSF) is a chronic, progressive and potentially malignant oral disorder with a high regional incidence and malignant rate. With the development of the disease, the normal oral function and social life of patients are seriously affected. This review mainly introduces the various pathogenic factors and mechanisms of OSF, the mechanism of malignant transformation into oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), and the existing treatment methods and new therapeutic targets and drugs. This paper summarizes the key molecules in the pathogenic and malignant mechanism of OSF, the miRNAs and lncRNAs with abnormal changes, and the natural compounds with therapeutic effects, which provides new molecular targets and further research directions for the prevention and treatment of OSF.
Keywords: epithelial–mesenchymal transition; lncRNAs; malignant transformation; miRNAs; myofibroblast; natural compounds; oral squamous cell carcinoma; oral submucous fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cirillo N., Duong P.H., Er W.T., Do C.T.N., De Silva M.E.H., Dong Y., Cheong S.C., Sari E.F., McCullough M.J., Zhang P., et al. Are There Betel Quid Mixtures Less Harmful than Others? A Scoping Review of the Association between Different Betel Quid Ingredients and the Risk of Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Biomolecules. 2022;12:664. doi: 10.3390/biom12050664. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

