Artificial Intelligence for Personalised Ophthalmology Residency Training
- PMID: 36902612
- PMCID: PMC10002549
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12051825
Artificial Intelligence for Personalised Ophthalmology Residency Training
Abstract
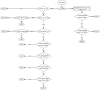
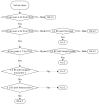
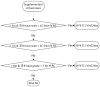
Residency training in medicine lays the foundation for future medical doctors. In real-world settings, training centers face challenges in trying to create balanced residency programs, with cases encountered by residents not always being fairly distributed among them. In recent years, there has been a tremendous advancement in developing artificial intelligence (AI)-based algorithms with human expert guidance for medical imaging segmentation, classification, and prediction. In this paper, we turned our attention from training machines to letting them train us and developed an AI framework for personalised case-based ophthalmology residency training. The framework is built on two components: (1) a deep learning (DL) model and (2) an expert-system-powered case allocation algorithm. The DL model is trained on publicly available datasets by means of contrastive learning and can classify retinal diseases from color fundus photographs (CFPs). Patients visiting the retina clinic will have a CFP performed and afterward, the image will be interpreted by the DL model, which will give a presumptive diagnosis. This diagnosis is then passed to a case allocation algorithm which selects the resident who would most benefit from the specific case, based on their case history and performance. At the end of each case, the attending expert physician assesses the resident's performance based on standardised examination files, and the results are immediately updated in their portfolio. Our approach provides a structure for future precision medical education in ophthalmology.
Keywords: contrastive learning; diagnosis of retinal conditions; precision education machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ocular Disease Intelligent Recognition ODIR-5K. [(accessed on 2 August 2022)]. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/andrewmvd/ocular-disease-recognition-odir5k.
-
- Gour N., Khanna P. Multi-class multi-label ophthalmological disease detection using transfer learning based convolutional neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021;66:102329. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102329. - DOI
-
- Pachade S., Porwal P., Thulkar D., Kokare M., Deshmukh G., Sahasrabuddhe V., Giancardo L., Quellec G., Mériaudeau F. Retinal Fundus Multi-disease Image Dataset (RFMiD) 2020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

