Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management
- PMID: 36902748
- PMCID: PMC10004032
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12051952
Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management
Abstract
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a common cardiac abnormality with a prevalence of 25% in the general population. PFO has been associated with the paradoxical embolism causing cryptogenic stroke and systemic embolization. Results from clinical trials, meta-analyses, and position papers support percutaneous PFO device closure (PPFOC), especially if interatrial septal aneurysms coexist and in the presence of large shunts in young patients. Remarkably, accurately evaluating patients to refer to the closure strategy is extremely important. However, the selection of patients for PFO closure is still not so clear. The aim of this review is to update and clarify which patients should be considered for closure treatment.
Keywords: PFO-associated syndromes; Patent foramen ovale (PFO); cryptogenic stroke; device closure; interatrial septal aneurysms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
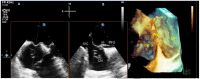
References
-
- Trabattoni D., Brambilla M., Canzano P., Becchetti A., Teruzzi G., Porro B., Fiorelli S., Muratori M., Tedesco C.C., Veglia F., et al. Migraine in Patients Undergoing PFO Closure: Characterization of a Platelet-Associated Pathophysiological Mechanism: The LEARNER Study. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2022;7:525–540. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.02.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

